Google has announced the release of an enhanced version of OSV-Scanner, a free tool designed to detect vulnerabilities in open-source code. Originally introduced in 2022 as an interface for the Open Source Vulnerability (OSV) database, OSV-Scanner has assisted developers in generating detailed vulnerability reports and strengthening the security of the Open Source ecosystem.
The latest iteration, OSV-Scanner V2.0.0, expands its capabilities through integration with OSV-SCALIBR, a sophisticated library for software composition analysis (SCA).
The scanner can now extract information from source code manifests and lock files, including deps.json for .NET, uv.lock for Python, bun.lock for JavaScript, and cabal.project.freeze for Haskell. Additionally, it supports artifact analysis, covering Node.js modules, Python packages, Uber JAR files for Java, and Go binaries.
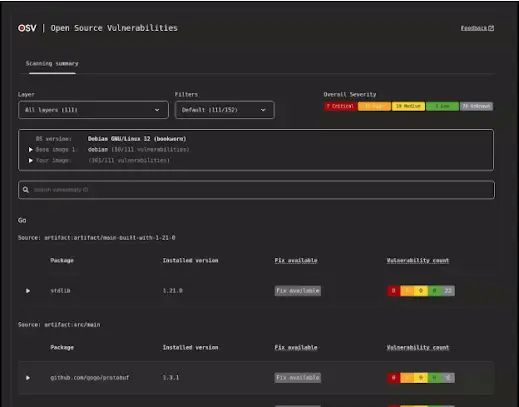
The tool now includes container image analysis for Alpine, Debian, and Ubuntu, offering insights into layer history, build commands, base image identification, and vulnerabilities that may not directly impact the container itself.
OSV-Scanner V2.0.0 introduces a new interactive report format, generating a local HTML file that presents remediation recommendations, criticality details of detected vulnerabilities, and filtering options based on package importance.
Support for automated vulnerability remediation has been added for Maven, allowing dependency updates in pom.xml while also accommodating private registries. Additionally, developers can leverage a machine-readable output format, simplifying the integration of OSV-Scanner into CI/CD pipelines.
Looking ahead, Google plans to expand support for new ecosystems, enable comprehensive scanning of all files within container images, integrate vulnerability reachability analysis, and introduce compatibility with the VEX (Vulnerability Exchange) standard.
OSV-Scanner V2.0.0 is now available on GitHub, and Google invites developers to contribute to its ongoing evolution.

