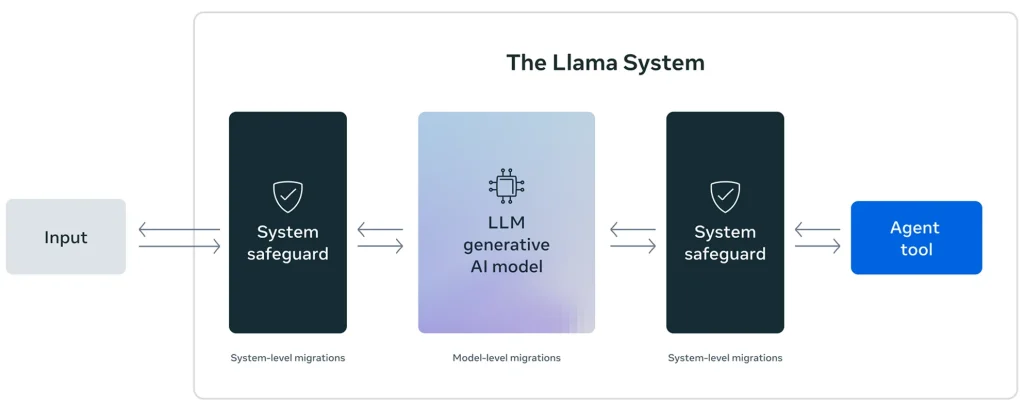
Meta has unveiled a new tool designed to fortify artificial intelligence systems against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. This innovation, dubbed LlamaFirewall, is released as open-source software and aims to detect and prevent a range of attacks — including malicious prompt injections, restriction bypasses, and the generation of unsafe code.
At the heart of LlamaFirewall lie three core protective components:
- PromptGuard 2 provides real-time detection of direct prompt injection attempts and manipulations.
- Agent Alignment Checks scrutinize the reasoning processes of AI agents to uncover potential hijacking attempts or covert attacks via indirect prompts.
- CodeShield is an online static analysis engine that prevents large language models from generating vulnerable code.
As detailed in the project’s technical documentation, LlamaFirewall is built on a modular architecture, enabling multilayered protection — from the moment input is received to the final response output. The framework is suitable for both simple chatbot applications and more complex autonomous agents.
In addition to LlamaFirewall, Meta has enhanced two other key tools. The refined version of LlamaGuard offers improved detection of prohibited content, while the latest edition of CyberSecEval assesses the resilience of AI systems against a broad spectrum of cyber threats.
Notably, CyberSecEval 4 introduces a new module called AutoPatchBench, which tests the capability of language models to automatically patch vulnerabilities in C and C++ code identified via fuzz testing. This module provides a standardized methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of such remediation efforts, helping developers discern the strengths and limitations of various approaches.
Meta has also launched Llama for Defenders, an initiative that grants developers and partners access to defensive tools with varying levels of openness. This flexibility allows the adaptation of security measures to specific use cases — such as detecting AI-generated content used in fraud or phishing campaigns.
All announcements were accompanied by a strong commitment to transparency. As part of its Private Processing program, the WhatsApp team is developing infrastructure that enables AI functionality without transmitting user data to public clouds. According to Meta, all architectural decisions undergo community-audited reviews and will continue to evolve in the open until the official release.