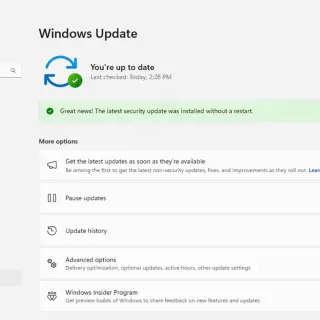
No More Reboots: Windows 11 Hotpatch Now Live
Microsoft has announced the rollout of its Hotpatch technology for Windows 11 Enterprise devices running version 24H2 on x64 architecture (AMD and Intel). As of April 2, 2025, this feature is available to all...