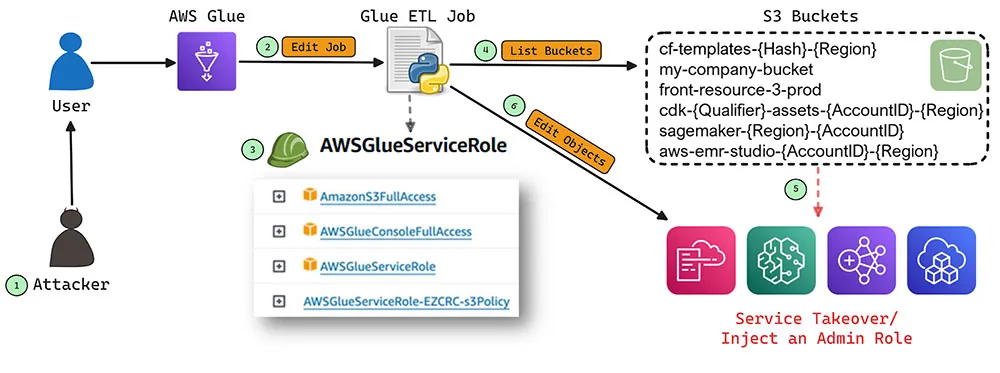
Experts have uncovered significant risks linked to default access policies within Amazon Web Services’ cloud infrastructure. These configurations—often automatically created when launching services like SageMaker, Glue, EMR, and Lightsail—not only enable threat actors to escalate privileges but also to gain control over other components of the AWS environment, potentially leading to full account compromise.
The core issue lies in the IAM roles that AWS services generate by default, which are excessively permissive—frequently granting full access to Amazon S3 storage. According to researchers at Aqua Security, such roles serve as convenient entry points for attackers who already possess minimal access; these roles can be exploited for lateral movement within the infrastructure and for deepening the attacker’s foothold.
Particularly concerning is the role named ray-autoscaler-v1, automatically created by Ray—a widely used open-source framework for scalable machine learning. This role also includes the AmazonS3FullAccess policy, opening the door to manipulation of the entire S3 storage content within the account.
Among the vulnerable scenarios potentially exploitable by attackers are the tampering of CloudFormation templates, injection of malicious scripts into EMR and SageMaker resources, the distribution of backdoors, and theft of IAM credentials. These vectors enable attackers not only to escalate their privileges but also to breach initially isolated segments of the environment.
The report’s authors emphasize that these attacks represent a broader threat landscape than the well-known “bucket monopoly” attacks, in which malicious actors occupy predictable S3 bucket names in unclaimed AWS regions. In this case, no guessing is required—the access is already present and sufficient to bypass inter-service isolation within a single AWS account.
Below are a few examples of AWS services that generate overly permissive roles:
- Amazon SageMaker: Automatically creates a role named
AmazonSageMaker-ExecutionRole-<timestamp>with a custom policy resembling full AmazonS3 access. - AWS Glue: Employs the
AWSGlueServiceRole, which holds similar privileges. - Amazon EMR: Generates the role
AmazonEMRStudio_RuntimeRole_<timestamp>, also assigned full access to S3.
One hypothetical attack scenario involves uploading a malicious machine learning model to Hugging Face. When deployed via SageMaker, the model could execute arbitrary code, granting access to additional services such as Glue, followed by privilege escalation and the injection of malicious CloudFormation templates.
Following the disclosure, Amazon revised the AmazonS3FullAccess policy for default roles. Nevertheless, security experts urge administrators not to rely solely on default configurations, and instead manually audit, restrict, and regularly reassess the permissions of existing roles.
In a related finding, a separate study by Varonis identified a vulnerability in the pre-installed AZNFS-mount utility on Microsoft Azure AI and HPC virtual machines. The flaw allowed a standard Linux user to escalate privileges to root via a misconfigured SUID binary. With elevated access, an attacker could mount new storage volumes, install malware, and pivot further through the network.
This issue was resolved in version 2.0.11 of the utility, released on January 30, 2025.