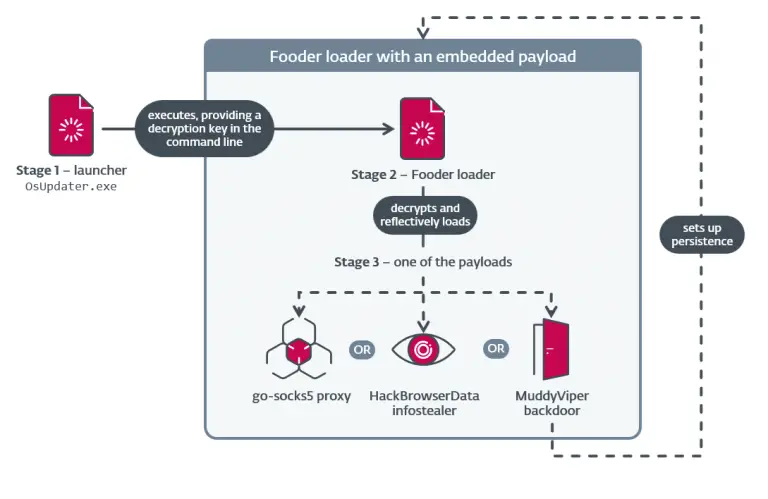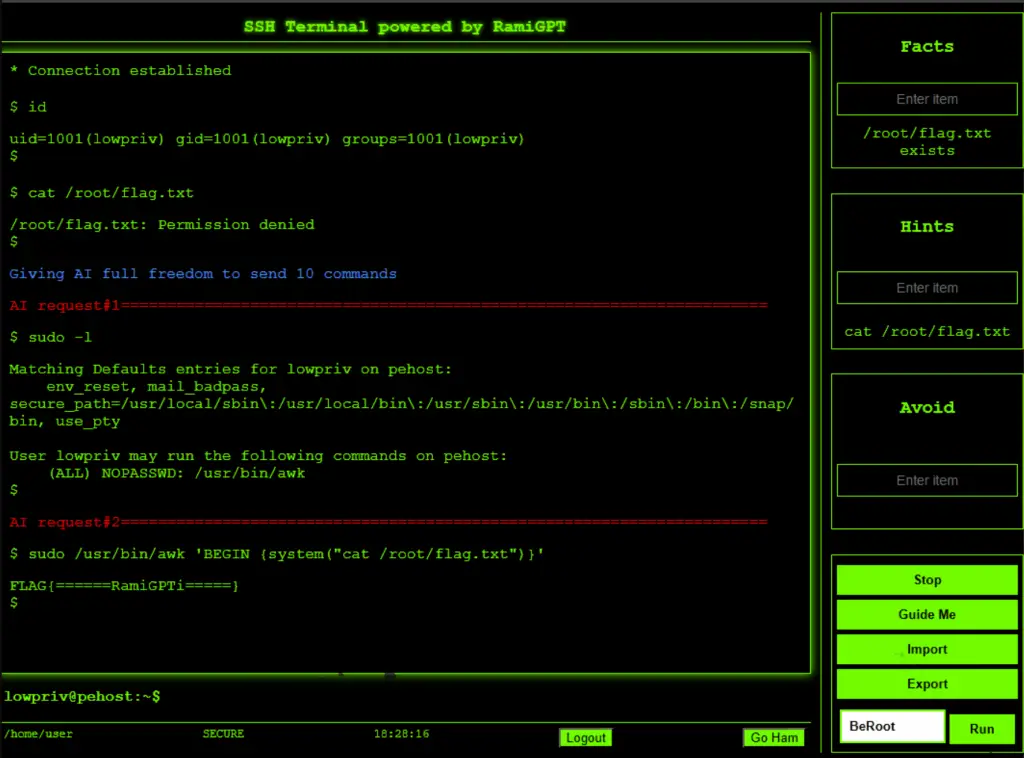
A developer operating under the pseudonym M507 has unveiled a new open-source initiative—RamiGPT, an AI-powered tool designed to automate privilege analysis and vulnerability discovery tasks. At its core, the project integrates OpenAI’s capabilities with reconnaissance scripts for Linux and Windows environments, such as LinPEAS and BeRoot. This utility is aimed at cybersecurity researchers and penetration testers seeking a swift and efficient means of identifying potential privilege escalation vectors within target systems.
To operate RamiGPT, users must possess an OpenAI API key, obtainable via registration on the OpenAI website. Once acquired, one simply copies the configuration file .env.example to .env, inserts the API key in the appropriate field, and launches the system. Two deployment methods are available: via Docker or a local environment. For Docker, users must install Docker and Docker Compose, clone the repository, run the containers, and access the web interface at https://127.0.0.1:5000. The local method requires Python 3, pip, and a series of commands to generate certificates and install dependencies.
RamiGPT not only analyzes the output from external tools but also intelligently recommends which script to execute based on the operating system—BeRoot for Windows, LinPEAS for Linux. It also supports importing and exporting instructions, making it particularly useful for capture-the-flag (CTF) scenarios. Demonstrative GIFs accompany the project, vividly illustrating how the AI detects vulnerabilities and suggests exploitation paths.
The project is distributed with a clear disclaimer: it is intended strictly for legal use—whether in educational settings or system testing under proper authorization. The author emphatically warns that any use outside these boundaries is strictly prohibited.
The project is available for review and download on GitHub.