Experts have released an in-depth analysis of the critical zero-day vulnerability CVE-2025-32756, which affects multiple Fortinet products. This flaw is currently being actively exploited in real-world attacks, posing a serious threat to corporate systems.
CVE-2025-32756, carrying a CVSS score of 9.8, is a stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability found within the administrative API. It allows unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via specially crafted HTTP requests. Several major Fortinet product lines are impacted, including FortiVoice, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder, and FortiCamera—across multiple versions.
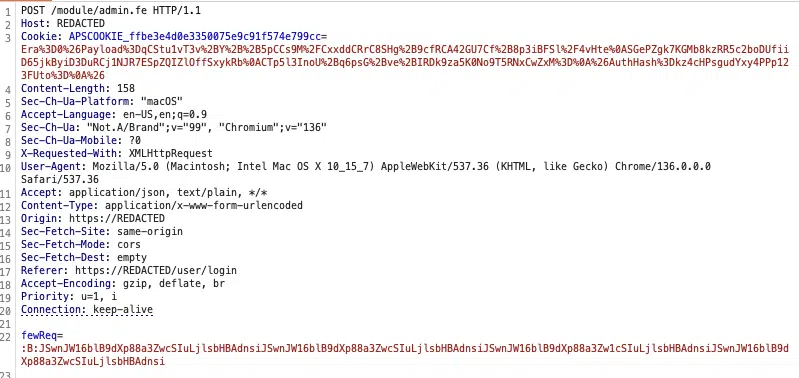
Technical analysis by Horizon3 revealed that the flaw lies in the cookieval_unwrap() function within the libhttputil.so library, which performs improper boundary checking when processing the APSCOOKIE value. In affected versions, this flaw allows the overflow of a 16-byte buffer, enabling attackers to overwrite critical stack values, including the return address. Recent patches have introduced constraints on the size of the AuthHash value, effectively mitigating the vulnerability.
Fortinet has confirmed that the vulnerability is under active exploitation, particularly targeting FortiVoice systems. According to the Product Security team’s observations, attackers have conducted network scans, exfiltrated credentials, and tampered with system logs. Notably observed behaviors include erasing crash logs, enabling FCGI debugging to intercept authentication attempts (including SSH logins), deploying malware, and configuring cron jobs to perpetually harvest credentials.
CVE-2025-32756 was added to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on May 14, 2025—just one day after Fortinet issued its initial advisory. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has mandated that all federal agencies remediate the vulnerability by June 4, underscoring the gravity of the threat.
Its rapid inclusion in the KEV list highlights both the severity and the wide-reaching implications of the flaw, especially for enterprises that rely heavily on Fortinet solutions. The situation is further exacerbated by the availability of a detailed technical proof-of-concept (PoC), and the low skill threshold required for exploitation—raising the likelihood of widespread attacks in the near future.
Fortinet strongly urges all affected customers to update their systems without delay. For those unable to implement immediate patches, a temporary workaround involves disabling the administrative HTTP/HTTPS interface. FortiVoice users are advised to upgrade to versions 7.2.1, 7.0.7, or 6.4.11, while FortiMail users should update to versions 7.6.3, 7.4.5, 7.2.8, or 7.0.9.