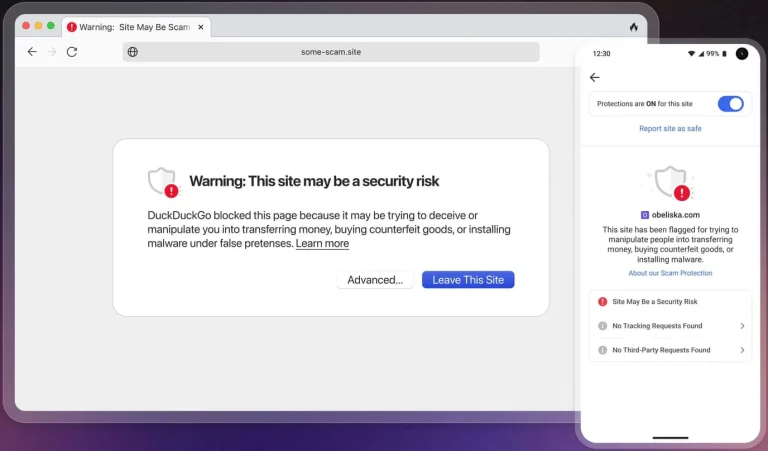
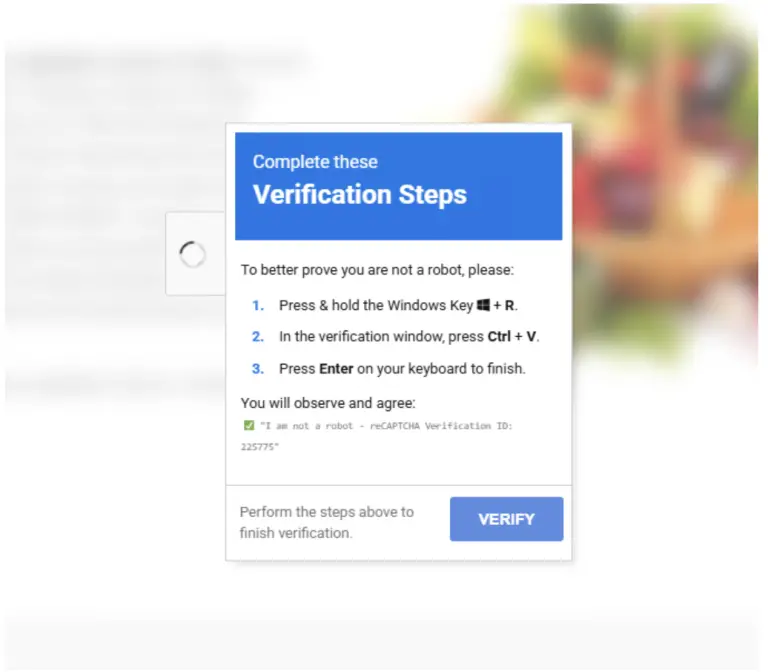
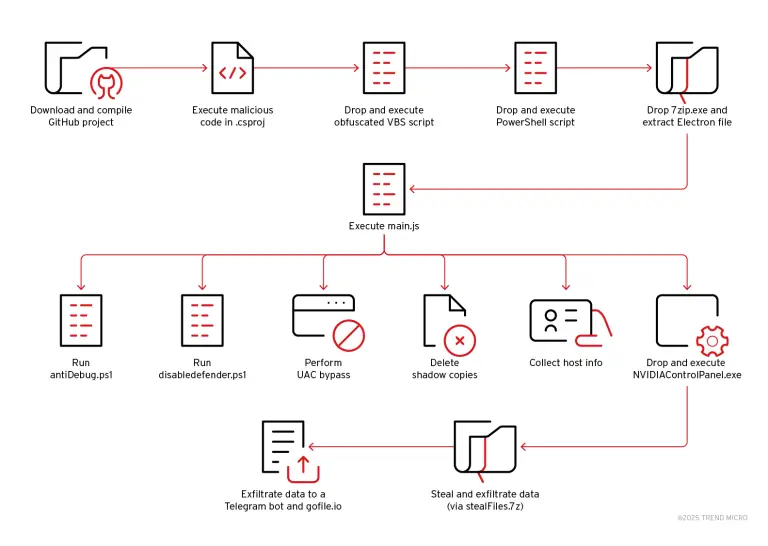
Output of the file command over the sha256 directory.
In recent times, cryptominers have begun to employ increasingly unconventional tactics, and a newly uncovered malicious campaign—identified by researchers at Darktrace and Cado Security—exemplifies this evolving trend. Unlike traditional attacks involving XMRig, the threat actors in this case are targeting Docker environments, deploying an unusual scheme tied to the Web3 platform known as Teneo.
The attackers launch a container image titled “kazutod/tene:ten”, hosted on Docker Hub. Since its upload, it has been downloaded 325 times. Upon execution, the image activates a Python script that undergoes 63 stages of unpacking before establishing a connection with the server teneo[.]pro. The code is heavily obfuscated, significantly complicating any efforts to analyze its behavior.
The distinguishing feature of this attack lies in its method of generating $TENEO tokens—not through standard cryptocurrency mining, but by passively connecting to the Teneo platform. This infrastructure is marketed as a decentralized system that rewards the aggregation of public data from social networks. However, in the observed campaign, no actual scraping occurs. Instead, the malware maintains a persistent WebSocket connection, sending periodic activity signals—so-called “heartbeats.” These heartbeats accrue Teneo Points, which can be converted into cryptocurrency.
The scheme mirrors a previous wave of attacks involving the deployment of 9Hits Viewer on compromised Docker instances. The goal then was to generate artificial web traffic to earn platform credits. This modus operandi closely aligns with proxyjacking—a practice in which victims unknowingly share their bandwidth in exchange for digital compensation.
The shift away from XMRig is largely due to its high detectability by modern security tools. In its place, attackers are embracing stealthier, less conspicuous mechanisms. While the profitability of this new model remains uncertain, its resilience to detection renders it particularly insidious.
These emerging cryptojacking strategies and infection vectors underscore how rapidly threats in the digital landscape are evolving. As a result, organizations must adopt increasingly agile and adaptive approaches to securing their cloud-native and containerized environments.