A scandal is unfolding in cyberspace surrounding a trojanized version of the XWorm RAT builder, which threat actors are actively disseminating via GitHub, Telegram, and various file-sharing platforms.
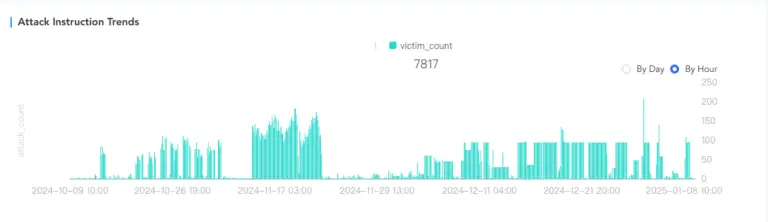
This malicious software primarily targeted novice cybersecurity enthusiasts who, following instructions from online guides, unknowingly downloaded and deployed it, oblivious to the hidden danger. To date, this malware has compromised over 18,000 devices worldwide.
XWorm RAT is designed to exfiltrate sensitive data, including browser information, Discord tokens, Telegram credentials, and system specifications of infected machines. One of its most insidious capabilities is leveraging Telegram as its command-and-control (C2) infrastructure.
Attackers issue commands through bots and exploit Telegram’s API to retrieve stolen data. Additionally, the malware is equipped with advanced evasion techniques, including virtual environment detection, Windows registry modifications to establish persistence, and full remote control over infected systems.
The highest concentration of infections has been recorded in Russia, the United States, India, Ukraine, and Turkey. Analysis reveals that over 1GB of browser data has been siphoned from more than 18,000 compromised devices. Furthermore, the malware takes screenshots of victims’ systems, extracts Telegram data, and even deploys additional executable payloads onto infected machines.
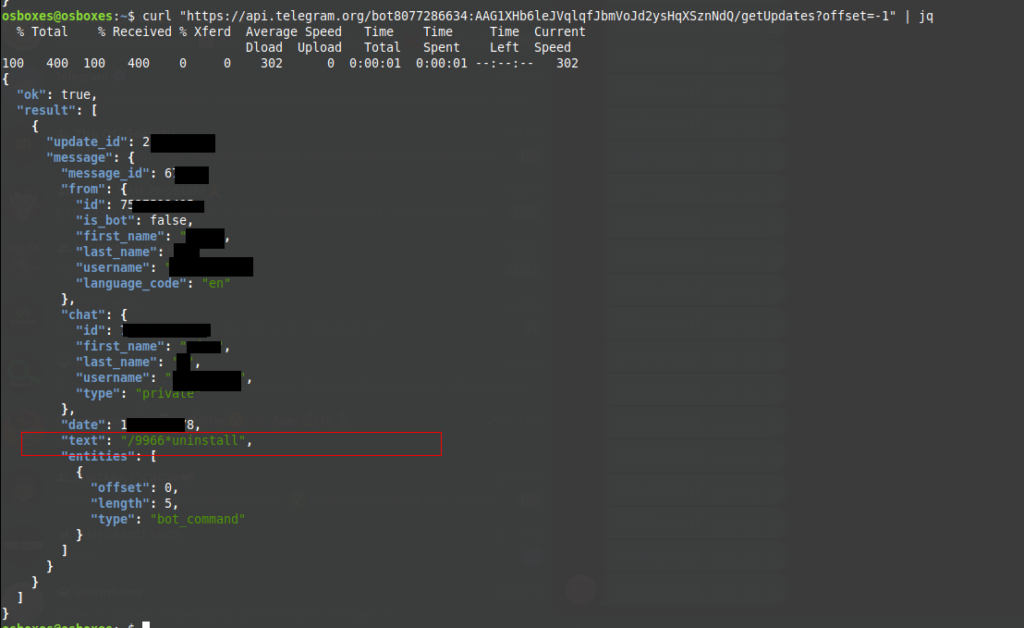
During the investigation, researchers uncovered an embedded “kill switch” within the XWorm RAT code, enabling them to issue a command to remove the malware from active devices. While this intervention partially mitigated the threat, many systems remained compromised due to their offline status or Telegram’s command rate limitations.
Key figures behind the operation were identified, with attackers utilizing Telegram accounts under the aliases “@shinyenigma” and “@milleniumrat,” as well as associated GitHub repositories and ProtonMail addresses. Leveraging this intelligence, cybersecurity researchers relayed the information to platform operators to facilitate the takedown of malicious accounts and content.
To safeguard against such threats, experts recommend implementing comprehensive detection and incident response solutions, restricting access to known malicious domains, regularly updating security systems, and conducting ongoing cybersecurity awareness training for employees.