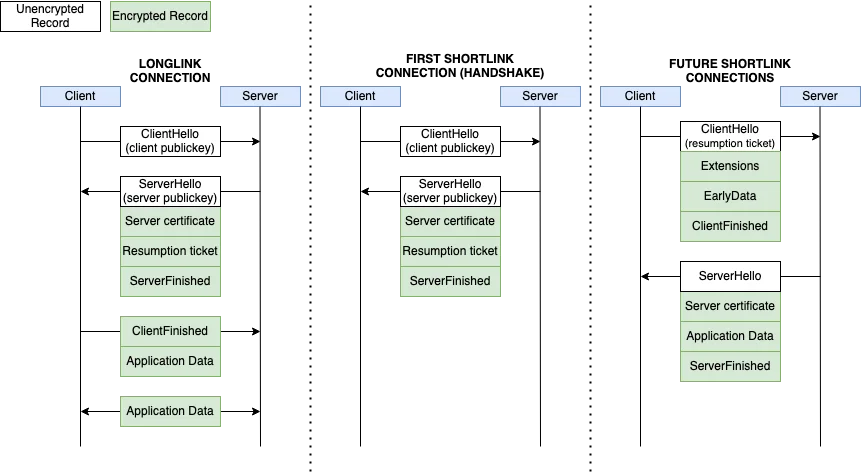
A recent study by Citizen Lab uncovered vulnerabilities in the networks of China’s most popular messaging app — WeChat. With over a billion monthly users, the program employs a proprietary protocol known as MMTLS, which is weaker than the standard TLS 1.3 from which it was modified.
The analysis revealed that WeChat uses a non-standard encryption method, known as MMTLS, which contains several cryptographic flaws. One of these vulnerabilities is the use of predictable initialization vectors (IVs), which could lead to the recovery of encryption keys and the exposure of confidential information. Furthermore, WeChat does not support Forward Secrecy, leaving past data vulnerable to decryption if the keys are compromised.
Researchers noted that earlier versions of WeChat relied on an even less secure encryption protocol, which is still partially used in modern iterations of the app. This raises concerns about the safety of user data, despite the absence of attacks capable of fully breaking the app’s encryption.
WeChat’s developers utilize their encryption system, a common practice in Chinese applications. However, these systems are often less reliable than internationally vetted standards like TLS.
The researchers have released tools for analyzing WeChat traffic, which will aid further research into the app’s security. This move is intended to encourage developers and cybersecurity experts to improve encryption and bolster the protection of user data.


