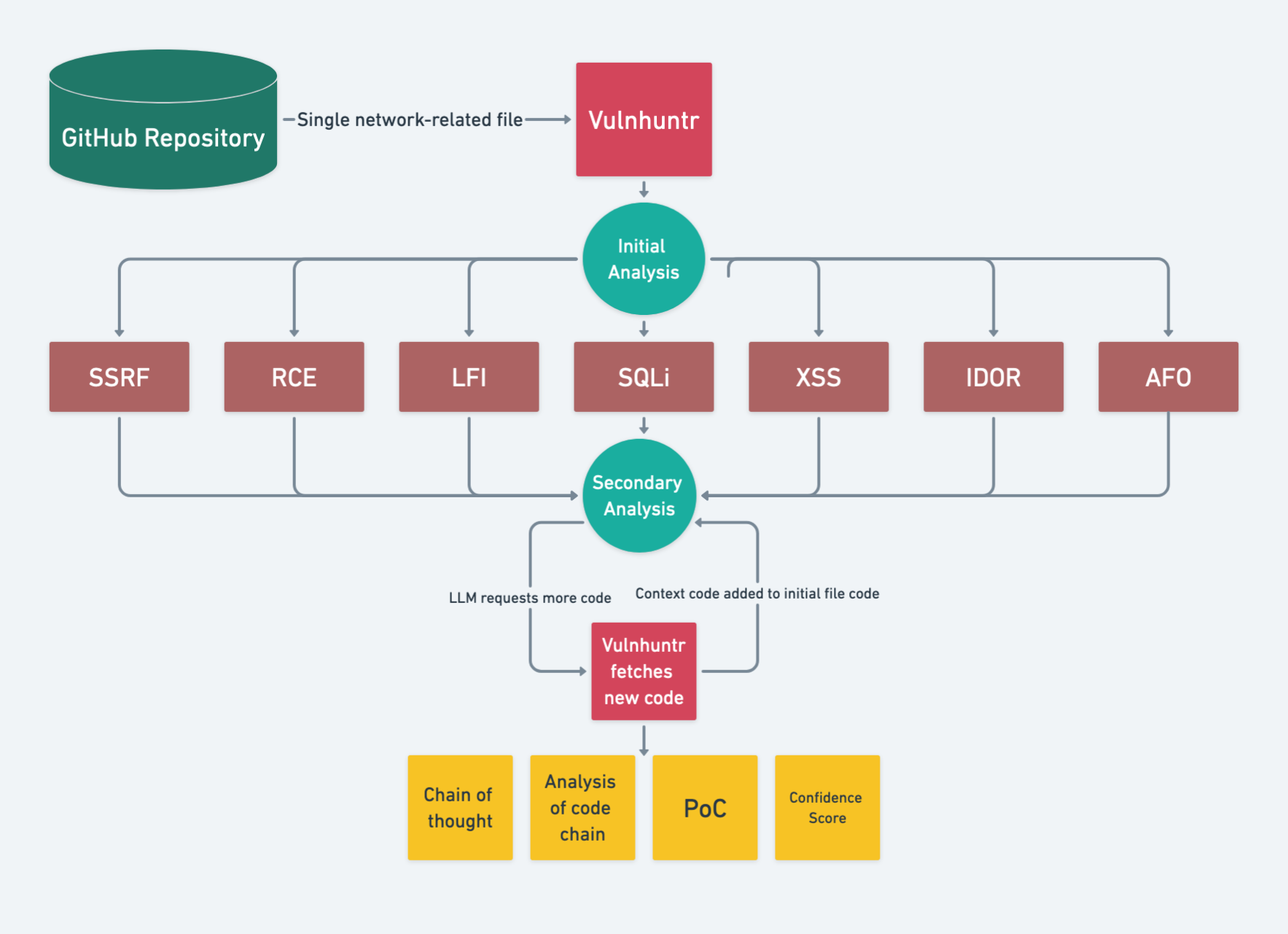
The new tool Vulnhuntr marks a breakthrough in vulnerability discovery within open-source projects. Developed by Protect AI, it harnesses the power of large language models (LLMs) to detect complex, multi-stage vulnerabilities, including remote zero-day exploits.
Vulnhuntr has already demonstrated impressive results, uncovering more than a dozen zero-day vulnerabilities within just a few hours of operation. Projects where vulnerabilities have been identified include gpt_academic, ComfyUI, FastChat, and Ragflow.
This tool distinguishes itself through its approach of breaking code into smaller segments for analysis, preventing LLM overload and significantly reducing false positives. Vulnhuntr conducts multiple code analyses, tracing a complete path from data input to server output and generating detailed reports, complete with exploit examples.
Its primary focus is on high-risk vulnerabilities: LFI, AFO, RCE, XSS, SQLi, SSRF, and IDOR. Special techniques, such as Chain of Thought and XML prompts, guide the LLM in narrowing the analysis to critical functions within the code.
Currently, Vulnhuntr supports only Python, but the developers plan to extend its capabilities to other programming languages. Despite its limitations, the tool’s performance far surpasses traditional static analyzers, offering more precise detection while reducing false positives.
The future of vulnerability hunting looks promising. As LLMs evolve, their context windows may reach millions of tokens, reducing reliance on static analysis. Nevertheless, Vulnhuntr will continue employing manual code parsing to minimize errors in vulnerability detection.
The tool is already available on the Huntr platform, where participants can use Vulnhuntr and receive rewards for contributing to the security of AI-driven projects. It can also be downloaded from GitHub.
Vulnhuntr significantly streamlines the process of identifying complex vulnerabilities, making it both more accurate and efficient. Not only does this tool enhance the security of individual projects, but it also strengthens the entire open AI ecosystem, supporting its resilience against emerging threats.


