Researchers at ESET have uncovered a previously unknown vulnerability in Mozilla products, which has been exploited in real-world attacks. This marks the second such incident in recent months; earlier, the CVE-2023-36884 vulnerability in Microsoft Word was similarly leveraged by malicious actors.
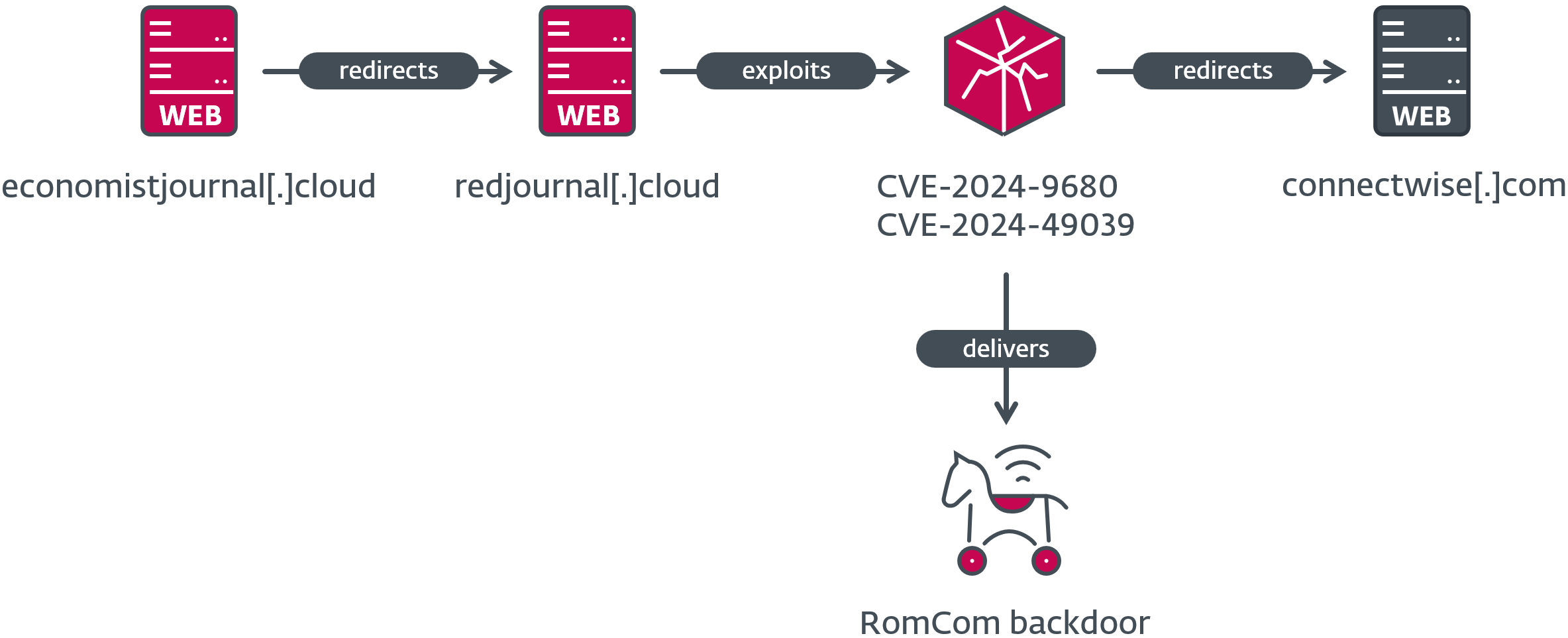
The newly identified flaw, CVE-2024-9680, carries a CVSS score of 9.8 and allows the execution of arbitrary code within the restricted context of Firefox, Thunderbird, and Tor Browser. When combined with another vulnerability in Windows (CVE-2024-49039, CVSS 8.8), attackers can escape the browser’s sandbox and execute code with the privileges of the current user. Exploitation requires only that a user visits a malicious webpage, after which malware is automatically downloaded and executed.
The vulnerability was first detected on October 8, 2024, and subsequent analysis revealed it stemmed from a use-after-free bug in Mozilla’s animation engine, enabling code execution. By October 9, Mozilla released security updates to address the issue. Additionally, a privilege escalation bug in the Windows Task Scheduler, which facilitated escaping the browser sandbox, was identified and patched by Microsoft on November 12.
The exploitation campaign involved fake websites redirecting victims to exploit servers. Successful attacks resulted in the deployment of a malicious backdoor capable of executing commands and downloading additional modules.
Analysis indicates that the attacks targeted users in Europe and North America between October and November 2024. The CVE-2024-9680 exploit functioned in Firefox, Tor Browser, and the Thunderbird email client, with the sandbox bypass achieved through the Windows vulnerability.
To protect users, Mozilla issued updates for all supported versions of its products. Patched versions include Firefox 131.0.2, Thunderbird 115.16, and Tor Browser 13.5.7.
This attack demonstrates a high level of sophistication, showcasing the attackers’ ability to exploit two previously unknown vulnerabilities to bypass standard security measures. The swift response from developers and the rapid release of patches were pivotal in mitigating the threat.