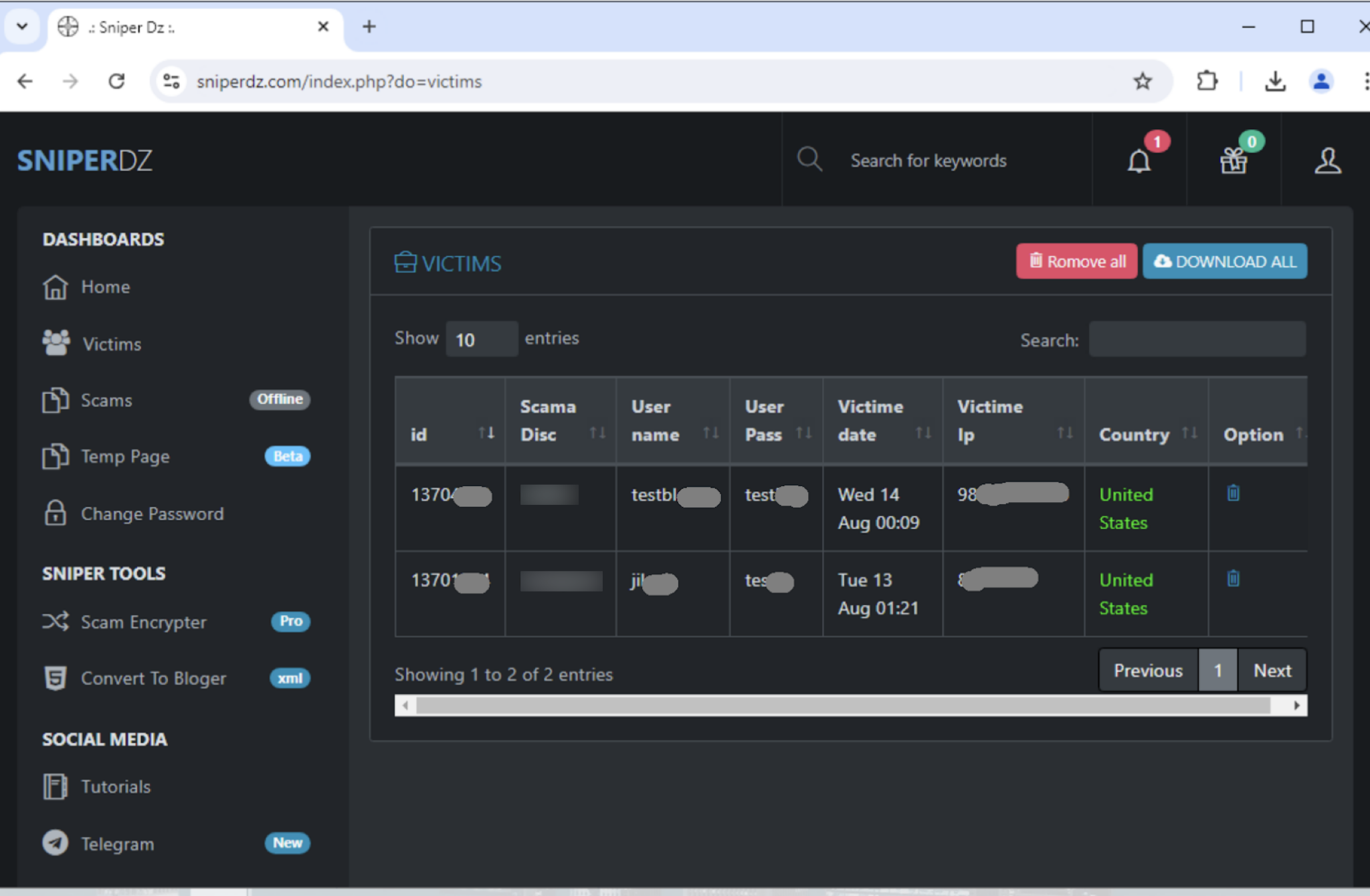
Admin panel showing stolen credentials of victim along with additional information such as victim’s IP address, country and time
The phishing platform Sniper Dz is responsible for creating over 140,000 phishing websites this year. Palo Alto Networks reports that this platform has gained popularity among cybercriminals by offering free phishing templates to its users. However, phishers using this service find themselves in a vulnerable position: the administrators of Sniper Dz receive copies of all stolen data.
Sniper Dz operates as a Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platform, providing an intuitive interface for creating phishing pages. To access the admin panel, users must register, after which they can select templates mimicking the websites of popular brands. The service offers two options: phishers can either host the pages on Sniper Dz’s servers or download templates for hosting on their own infrastructure.
Remarkably, Sniper Dz offers its services free of charge. This may be explained by the fact that the platform extracts stolen data through built-in tracking mechanisms, allowing the administrators to collect victims’ credentials, including those using their own servers to host phishing pages.
To obscure its operations, Sniper Dz conceals phishing pages behind public proxy servers. This makes it harder to detect fraudulent sites, as they appear to be legitimate resources. Additionally, the attackers actively exploit legitimate SaaS platforms to host phishing pages, helping them bypass security systems due to the strong reputations of these domains.
Most phishing pages associated with Sniper Dz target users of social networks and popular online services in the United States. The research notes that the platform’s infrastructure is regularly updated, and the number of phishing sites surged dramatically in mid-2024.
It is important to note that the platform not only collects stolen data but also redirects victims to other malicious resources, where they may be offered unwanted software or malicious browser extensions.
Phishing activity linked to the Sniper Dz platform continues to grow, posing a serious threat to internet users.


