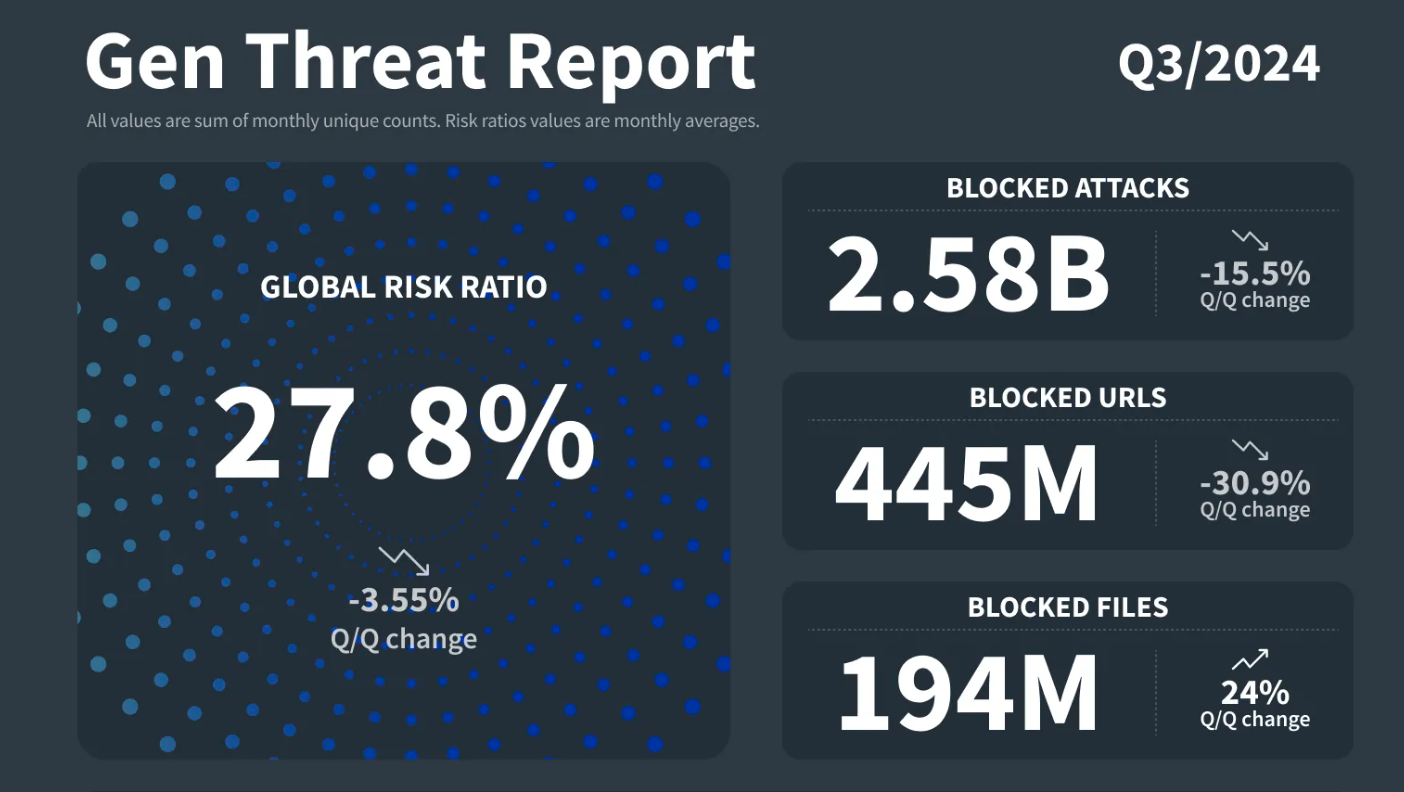
A new Gen Digital security threat report for Q3 has revealed a rapidly evolving threat landscape. Key trends include a surge in social engineering attacks, a significant increase in ransomware incidents, and the emergence of new malware targeting both desktop systems and mobile devices.
The report highlights the rise of “self-hack” attacks, which surged by an astounding 614% compared to the previous quarter, with over 2 million incidents thwarted. This technique manipulates users through social engineering to unwittingly compromise their own devices. Examples include fake CAPTCHAs that secretly infect systems with malicious scripts.
These attacks are often propagated via fake tutorial videos on YouTube, fraudulent browser updates, and deceptive software troubleshooting guides. Cybercriminals also coax users into disabling antivirus programs to avoid detection. Such campaigns are frequently employed to deploy infostealers, which harvest sensitive user data, including passwords and financial information.
Ransomware attacks saw a 24% increase, with particular concern surrounding Lumma Stealer, malware distributed through the MaaS (Malware-as-a-Service) model. This tool has fueled a 39% uptick in infostealer activity. These threats effectively bypass existing security measures, making them especially dangerous.
On mobile devices, banking Trojans and spyware dominate the threat landscape. The Rocinante virus, designed to steal banking credentials, has gained significant traction in Brazil. Meanwhile, in Europe, new versions of Octo and TrickMo have emerged, exploiting vulnerabilities to extract user data. Spyware such as NGate, which steals NFC data to facilitate ATM fraud, has become a major threat in the Czech Republic.
Cryptocurrency scams continue to rise, bolstered by deepfake technology. Criminals create convincing videos featuring well-known personalities to promote fraudulent investment schemes. These methods enable attackers to reach and manipulate large audiences, convincing them to invest in fictitious cryptocurrency projects.
The third quarter of 2024 has underscored the increasing complexity of cyber threats, with user deception remaining the primary weapon of choice for attackers. Experts recommend regular system updates, vigilance against suspicious links, and the use of robust antivirus solutions to enhance protection.


