Over 22,000 servers using the popular website management platform CyberPanel were recently targeted in an attack exploiting a critical vulnerability. The incident led to the disabling of nearly all vulnerable servers and the deployment of the ransomware PSAUX.
Security researcher DreyAnd discovered that CyberPanel versions 2.3.6 and likely 2.3.7 contain several serious vulnerabilities that allow for remote code execution (RCE) with full server access. Among these vulnerabilities are weak authentication mechanisms, command injection flaws, and security filter bypasses, enabling attackers to execute commands with root privileges.
According to the researcher, the identified vulnerabilities allow unauthorized access to pages and malicious command injection due to inadequate filtering on certain routes. DreyAnd created a proof-of-concept exploit demonstrating how to take control of a server using the discovered vulnerabilities.
The researcher informed CyberPanel’s developers of the issue on October 23, and a patch addressing the authentication flaws was released the same day. Within half an hour of receiving the report, CyberPanel’s creator, Usman Nasir, announced the release of version 2.3.8, which addresses the vulnerabilities. The development team is actively assisting users with updates and addressing issues related to the attack’s aftermath.
However, the threat remains relevant. According to the leak search engine LeakIX, over 22,000 unpatched servers were accessible online at the time the vulnerability was reported, with approximately 10,000 located in the United States. Shortly after the attacks began, most of these servers became unavailable—likely compromised and infected with PSAUX. At the time of the attack, over 152,000 domains and databases were managed through CyberPanel.
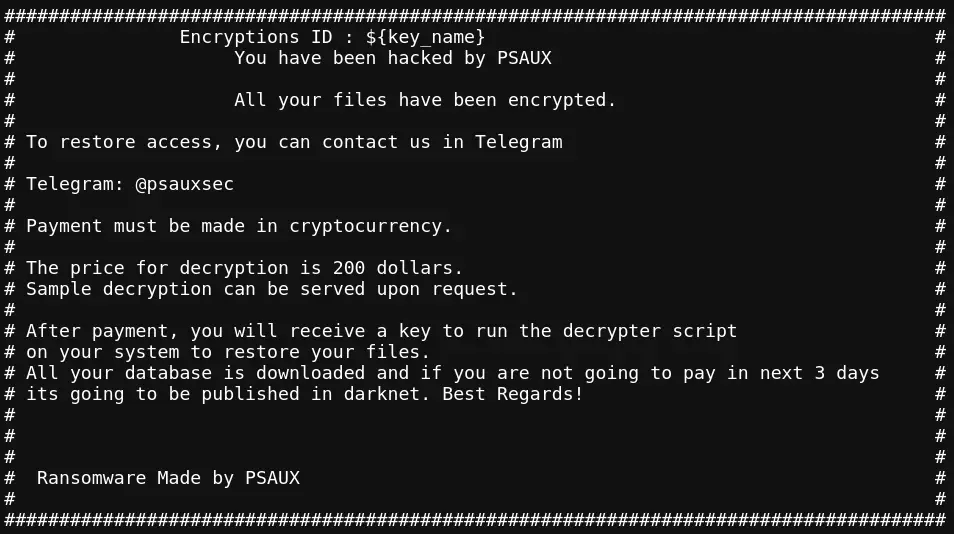
PSAUX is ransomware designed to encrypt files and demand payment. It generates unique encryption keys stored on the system, and encrypted files receive the extension “.psaux.” Victims find a ransom note with instructions on accessing their files.
Researchers analyzed the attackers’ tools and discovered that they used specialized scripts—“ak47.py” to exploit the vulnerability and “actually.sh” to encrypt files. Fortunately, due to an error in the encryption algorithm, experts were able to develop a free decryption tool.
At the time of publication, it was also revealed that, in addition to PSAUX, two other types of ransomware began exploiting the CyberPanel vulnerability, adding “.locked” and “.encrypted” extensions to affected files.
Experts strongly recommend updating CyberPanel to the latest version available on GitHub as soon as possible. This step will help mitigate risks and secure data against potential threats.


