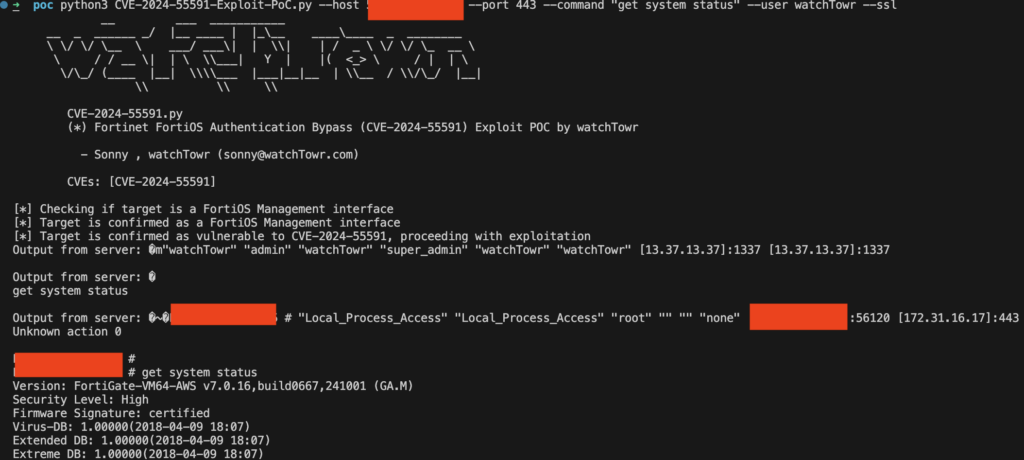
A critical vulnerability has been discovered in Fortinet FortiOS, enabling attackers to bypass authentication and escalate their privileges to super-administrator on FortiGate devices. Tracked as CVE-2024-55591, this flaw is already being actively exploited in the wild, with tens of thousands of devices estimated to be at risk.
The vulnerability originates from jsconsole, a web-based command execution console embedded within the FortiOS management interface. This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to create new administrative accounts, effectively granting them full control over targeted devices.
Researchers at Arctic Wolf reported that FortiGate attacks had commenced well before the public disclosure of the vulnerability. Meanwhile, Fortinet had privately notified its customers about the issue without revealing technical details.
Further analysis reveals that CVE-2024-55591 is linked to improper handling of the local_access_token parameter, a crucial element in the authentication process. By exploiting this weakness, attackers can:
- Bypass WebSocket connection validation
- Manipulate session context
- Obtain super-admin privileges
Additionally, researchers discovered a race condition between WebSocket and Telnet connections, allowing attackers to execute commands before authentication is fully completed.
Exploiting this vulnerability enables attackers to execute arbitrary commands via the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the affected device. This grants full administrative control, allowing them to:
- Modify system configurations
- Create and manage user accounts
- Compromise VPN infrastructure
Given that many enterprises rely on Fortinet FortiGate as their primary VPN solution, this flaw poses a severe security risk.
Fortinet has released patches addressing the vulnerability in affected versions of FortiOS and FortiProxy, but a significant number of devices remain unpatched. The Shadowserver research group has identified nearly 50,000 vulnerable instances still exposed to potential exploitation.
Security experts strongly advise organizations to:
- Immediately apply the latest security updates
- Disable admin console access from the open internet
In the wake of this incident, researchers have identified additional security flaws in FortiOS, though they have yet to be assigned public CVE identifiers. Experts warn that Fortinet’s authentication mechanisms may still contain other weaknesses, which could lead to further attack vectors in the future.
While Fortinet has not commented on these findings, remediation efforts are expected in upcoming security updates.
The watchTowr research team has released a vulnerability scanning tool, enabling administrators to assess their systems for exposure to CVE-2024-55591. However, malicious actors are already actively exploiting the flaw, making immediate remediation a top priority for all FortiGate device owners.