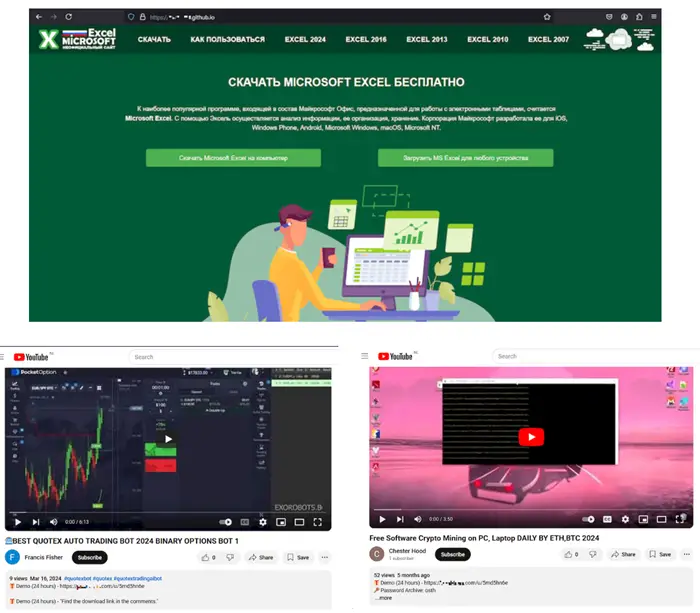
Experts at Dr.Web have uncovered a large-scale campaign to distribute malware designed for cryptocurrency mining and theft. The attackers disguised the malicious software as office applications, game cheats, and bots for online trading, distributing them through fake pages on GitHub and YouTube.
The malware identified by the specialists was camouflaged as a Windows system component (StartMenuExperienceHost.exe), responsible for managing the Start Menu. The malware actively communicated with a remote host and launched the command-line interpreter cmd.exe to execute further actions.
The cybercriminals employed the legitimate network utility Ncat, typically used for data transmission via the command line. By detecting this element, the researchers were able to reconstruct the sequence of events and halt further distribution.
The infection source was fake GitHub and YouTube pages, where users downloaded a self-extracting archive, protected by a password. Antivirus software cannot scan such archives due to their encryption. Inside the archive were temporary files, which were extracted into the system folder and initiated the execution of malicious scripts.
Following the execution of the scripts, the AutoIt library was loaded, which facilitated the launch of malicious scenarios. During the attack, the perpetrators also employed the Process Hollowing technique, whereby trusted system processes were replaced with malicious code. This allowed the hackers to mine cryptocurrency covertly and replace wallet addresses in the clipboard, redirecting funds to their own accounts. It is estimated that the attackers gained over $6,000 through these means.
The campaign affected over 28,000 individuals, primarily in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, and Turkey. To protect against such threats, it is recommended to download software only from official websites, use antivirus software, and avoid pirated versions of applications.


