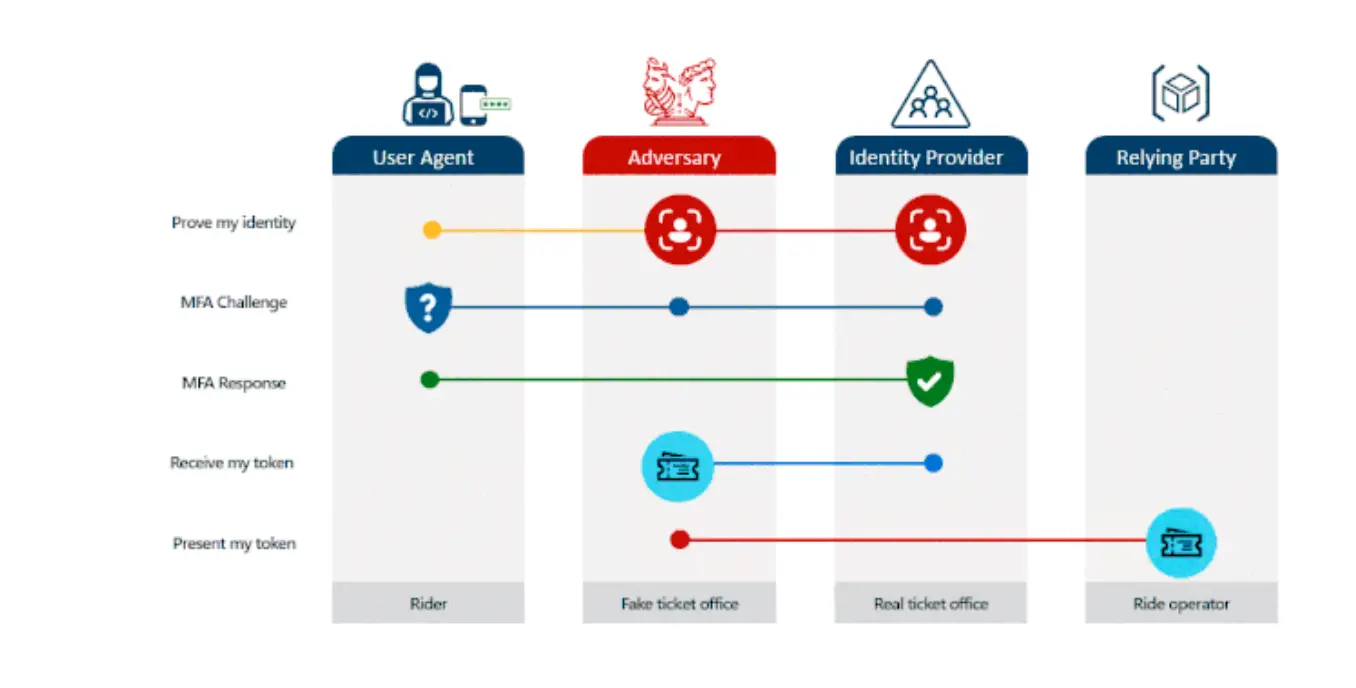
Microsoft has published an in-depth analysis of Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) phishing attacks, which are becoming increasingly prevalent due to the widespread adoption of multi-factor authentication (MFA). The company underscored the critical need for advanced protective measures to counter such threats.
AiTM phishing represents a sophisticated evolution of cyberattacks, wherein attackers create fraudulent websites, steal account credentials—including MFA codes—and use them to access legitimate services. This enables them to obtain the access tokens required to bypass MFA safeguards.
As a comprehensive solution, Microsoft advocates transitioning to “phishing-resistant” authentication methods, such as Passkeys. These methods leverage cryptographic principles to eliminate the risk of credential interception. Passkeys are device-specific, tied to unique URLs, and require user identity verification, such as biometric authentication.
For users unable to implement Passkeys immediately, Microsoft recommends additional security measures. These include using the Microsoft Authenticator app with geolocation and Number Matching features, restricting access to managed devices, and enforcing conditional access policies that verify network boundaries.
Furthermore, Microsoft advises organizations to adopt anomaly detection technologies, such as Entra ID Protection and Microsoft Defender. These tools monitor suspicious activities, such as login attempts from unusual IP addresses or unexpected token requests. Detected threats can trigger automatic session blocks, preventing unauthorized access.
For organizations dealing with the aftermath of AiTM attacks, Microsoft provides investigative and risk mitigation tools, including Microsoft Sentinel and Defender XDR. These solutions facilitate incident analysis, threat source identification, and the prevention of further data breaches.
Microsoft experts emphasize that implementing these combined measures significantly reduces the likelihood of successful AiTM attacks, rendering such intrusion methods exceedingly difficult to execute.


