Qualys has identified a new active campaign of the Mirai botnet, dubbed the Murdoc Botnet. The investigation revealed that attackers are exploiting vulnerabilities in AVTECH devices and Huawei HG532 routers to construct an extensive botnet network. This attack is distinguished by its enhanced mechanisms for propagation and device infection.
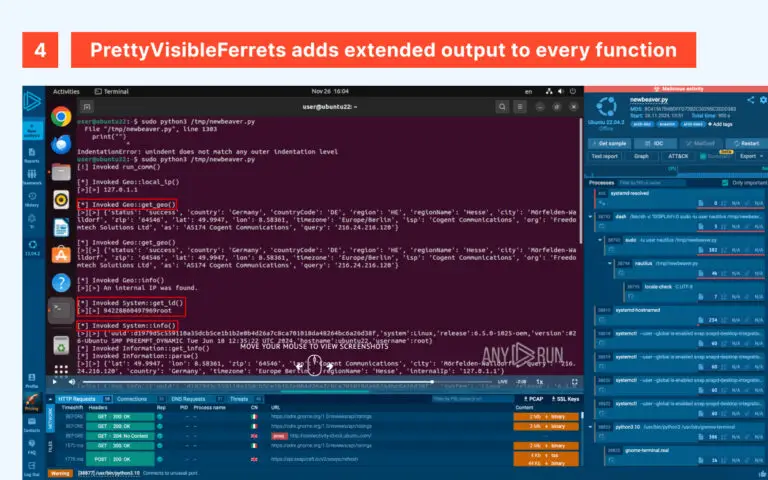
The Murdoc Botnet campaign commenced in July 2024. Analysis indicates the use of ELF executables and Shell scripts to deploy malware samples onto targeted devices. Similar methods have been observed in previous attacks throughout 2024.
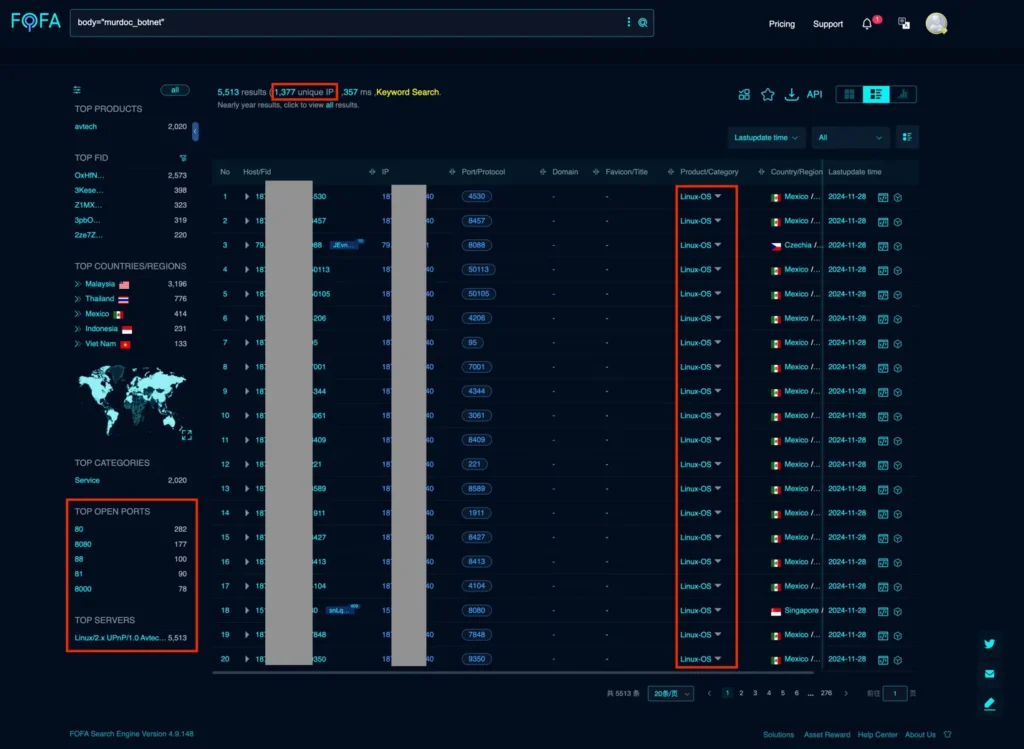
Experts identified over 1,300 IP addresses involved in this campaign, along with more than 100 command-and-control servers distributing malicious payloads. These servers execute the attackers’ commands, enabling efficient management of the infected network.
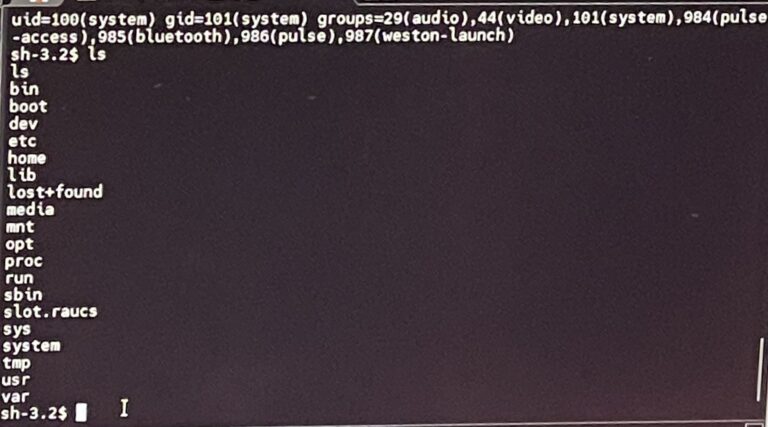
The Murdoc Botnet specifically targets devices with known vulnerabilities, such as CVE-2024-7029 and CVE-2017-17215. The investigation confirmed the use of commands to download malicious files onto devices, including IP cameras and IoT devices. The attackers also heavily rely on basic Linux commands to execute their malicious scripts.
During the campaign, more than 500 samples, including ELF files and Shell scripts, were analyzed. These were used to automate the deployment of new Mirai variants onto devices, highlighting the large-scale nature of the attack.
Geographic analysis of the attacks revealed that Malaysia, Thailand, Mexico, and Indonesia were the most affected regions, underscoring the campaign’s global scope.
Protection recommendations include regularly updating systems, monitoring suspicious network activity, and exercising caution when executing scripts from unknown sources. Adhering to cybersecurity best practices and promptly addressing vulnerabilities can significantly mitigate the risks posed by such threats.