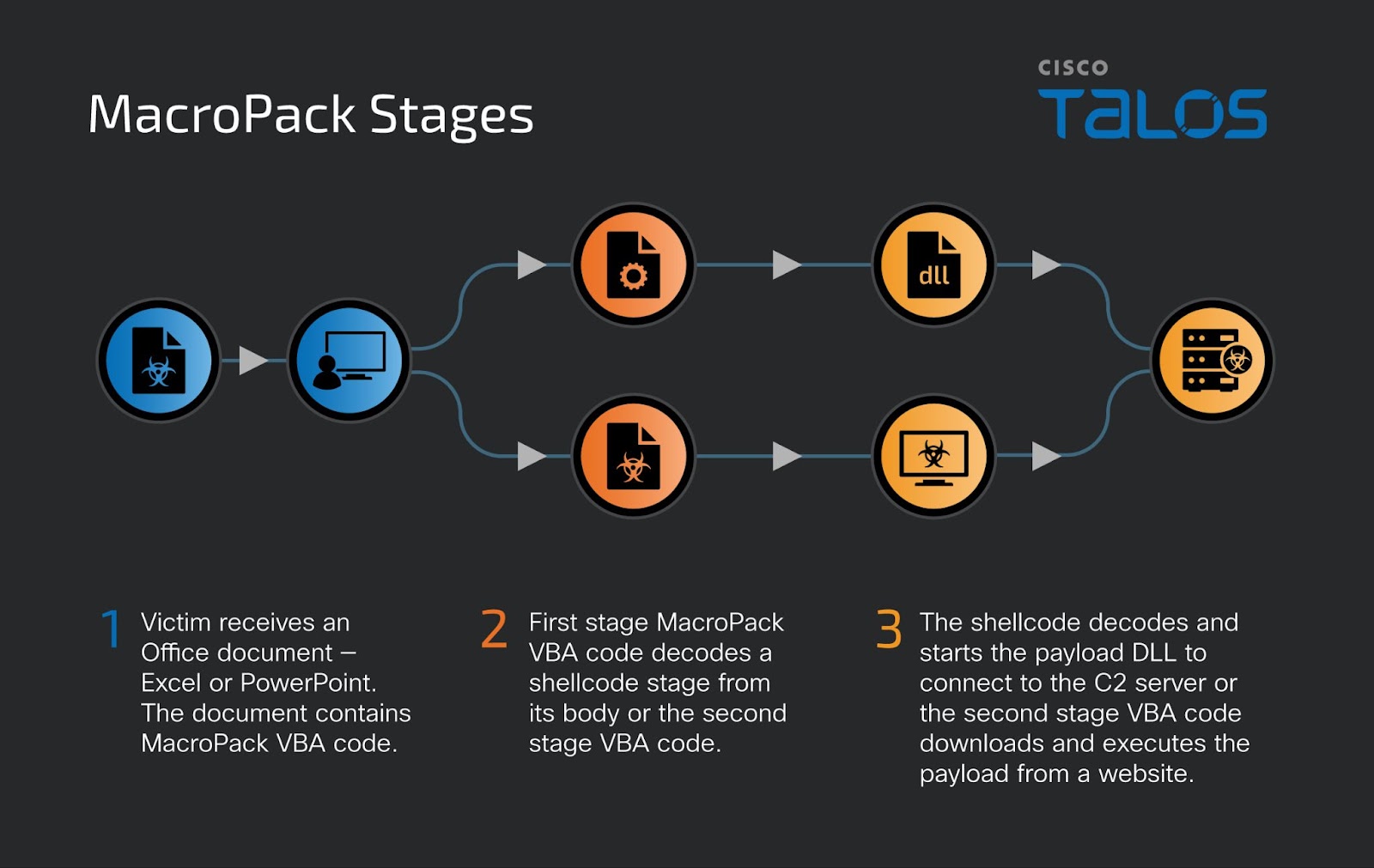
Stages of execution for discovered MacroPack-generated documents
Cisco Talos experts have uncovered that the red team framework MacroPack is being actively exploited by cybercriminals to disseminate malware such as Havoc, Brute Ratel, and the PhantomCore RAT trojan.
During the analysis of malicious document uploads on the VirusTotal platform, samples from various countries, including the United States, China, and Pakistan, were identified. The documents varied in complexity, lures, and infection methods, indicating a wide range of cyber threats tied to MacroPack usage.
Developed by a French programmer, MacroPack is a specialized tool designed for Red Team simulations and adversary emulation exercises. The software offers advanced features, such as antivirus evasion, anti-reversing techniques, and the ability to generate documents with code obfuscation. These capabilities enable the concealment of malicious VB scripts and bypassing of static analysis, significantly complicating detection.
Researchers noted that hackers frequently employ the paid version, MacroPack Pro, which incorporates distinctive VBA subroutines into the documents. While not inherently malicious, these subroutines serve as indicators that the document was crafted using the Pro version of the framework. Opening such a document triggers the initial stage of the attack, wherein VBA code loads a malicious DLL that connects to a C2 server.
The analysis of activity revealed several notable clusters. In China, Pakistan, and the U.S., various campaigns utilizing documents created with MacroPack were observed:
- In China (May–July 2024), documents prompting users to enable macros led to the download of Havoc and Brute Ratel malware, which communicated with C2 servers located in China.
- In Pakistan, military-themed documents masqueraded as official letters from the Pakistan Air Force. These files leveraged Brute Ratel to exfiltrate malicious data via DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and Amazon CloudFront.
- In the U.S. (March 2023), a malicious document posed as an encrypted form for updating the NMLS (National Mortgage Licensing System) and employed functions generated by a Markov chain to evade antivirus detection. The document contained code that checked for sandbox environments before downloading an unknown piece of malware.
Since 2022, Brute Ratel has become a favored alternative to Cobalt Strike among hackers. The tool is widely used to circumvent EDR systems and antivirus protections. Furthermore, some ransomware groups have adopted a cracked version of the tool to conduct stealthy attacks.


