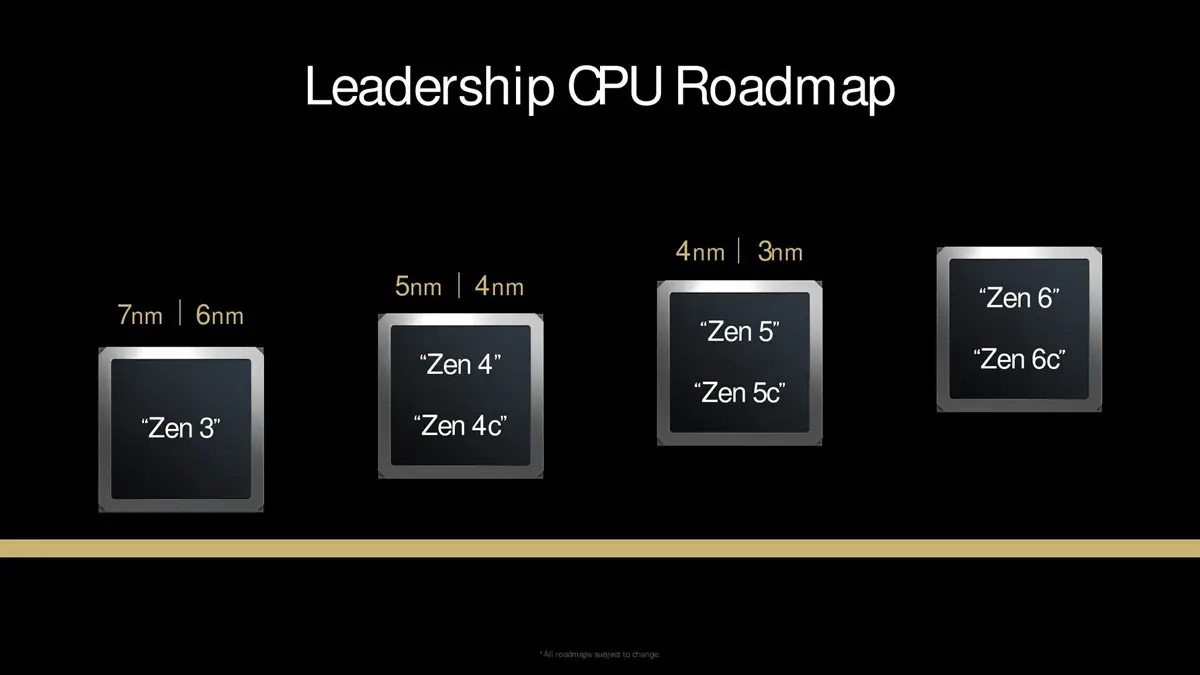
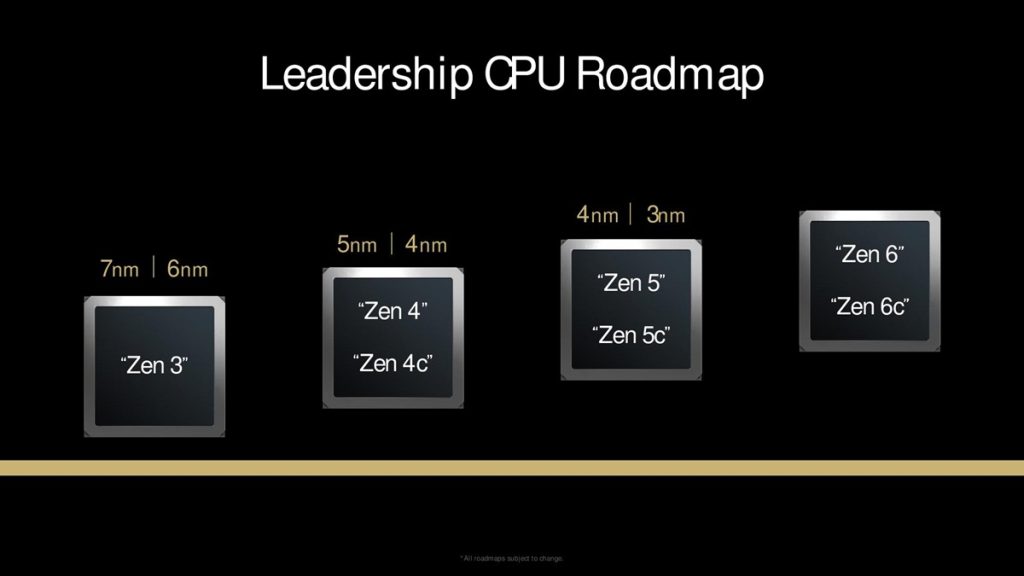
At the “AMD Tech Day 2024” held in Los Angeles, USA, AMD updated its CPU technology roadmap, revealing for the first time that the Zen 6 series architecture would follow the Zen 5 series. The Zen 6 series will be divided into Zen 6 and Zen 6c, featuring the so-called “big and little cores.” However, AMD did not mention the release date for the Zen 6 series architecture or confirm the manufacturing process node to be used.
According to a report by ComputerBase, AMD’s Chief Technology Officer, Mark Papermaster, emphasized at the conference that AMD is not only proud to present the roadmap but is also implementing it and will continue to maintain a leading position. He reiterated the commitment made at COMPUTEX 2024 that the AM5 platform would be supported until at least 2027. Additionally, there was a brief mention of the Zen 7 series architecture, which is already under development by a dedicated team.
Based on the current pace of AMD’s architecture updates on the AM5 platform, the Zen 6 series architecture is expected to continue using the AM5 platform. When it comes to the Zen 7 series architecture, there might be a change to a new socket. Although there are speculations that the AM5 platform could span four generations of architecture, AMD has not provided any specific commitments. It is speculated that the next-generation platform (AM6?) might introduce support for DDR6 and PCIe 6.0, along with updated standards for memory, storage, and expansion.
Rumors suggest that the internal codename for the Zen 6 architecture is “Morpheus” and it will be manufactured using a 2/3nm process. The Zen 6 series architecture includes three CCD configurations: 8-core (Zen 6), 16-core (Zen 6c), and 32-core (Zen 6c extended). AMD may launch the Zen 6 architecture in the second quarter of 2025, with production by the end of 2025, but mass production could be delayed until 2026.
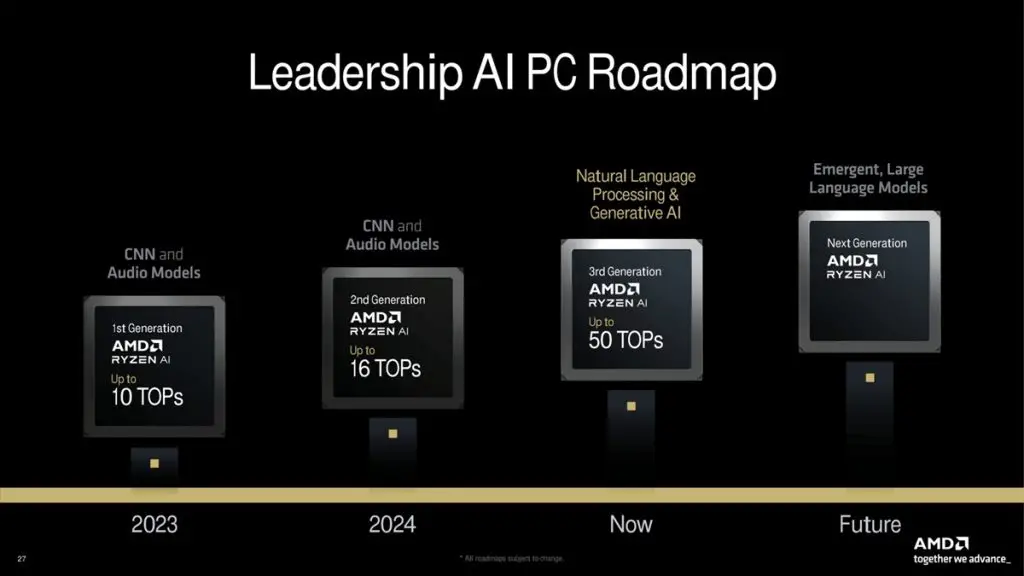
Moreover, AMD will focus on AI acceleration. The current Ryzen AI 300 series processors’ XDNA 2 architecture NPU offers 50 TOPS of computational power, insufficient for more advanced tasks. In the future, users can expect more advanced features, such as proxy AI, where artificial intelligence not only passively responds to human input but can also independently initiate actions.


