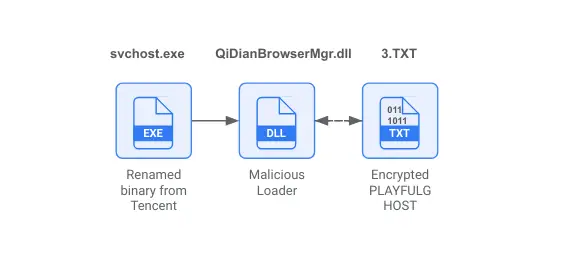
Renamed Tencent binary loads malicious DLL to launch PLAYFULGHOST
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a new strain of malware named PLAYFULGHOST, equipped with extensive capabilities for data collection. Its features include keylogging, screen and audio capture, remote access via command-line interface, and the ability to transfer and execute files.
According to the Google Cloud Security team, PLAYFULGHOST bears similarities to Gh0st RAT, a well-known remote administration tool whose source code was leaked back in 2008. The primary infection vectors for PLAYFULGHOST are phishing emails and SEO poisoning techniques.
In one phishing scenario, attackers used a RAR archive disguised as an image file with a “.jpg” extension. Upon extraction and execution, the archive installs a malicious executable, which subsequently downloads and activates PLAYFULGHOST from a remote server.
Another infection method through SEO poisoning involves a compromised installer for LetsVPN, which embeds intermediary malicious code responsible for deploying the malware’s components.
To execute the attack, adversaries employ techniques such as DLL hijacking and DLL sideloading to run a malicious library that loads and decrypts PLAYFULGHOST directly into the device’s memory. In more sophisticated cases, multiple files are combined to create a malicious DLL using a modified version of the Curl utility.
PLAYFULGHOST establishes persistence through registry keys, task scheduler entries, the startup folder, and Windows services. It collects keystrokes, screenshots, audio recordings, account credentials, clipboard contents, system metadata, and information about installed antivirus products. The malware can also disable keyboard and mouse inputs, erase Windows event logs, clear browser caches, remove messaging app profiles, and perform other destructive operations.
Additionally, PLAYFULGHOST can deploy auxiliary tools, including Mimikatz and rootkits designed to conceal files and processes. One such tool, Terminator, exploits driver vulnerabilities to terminate security processes. During the analysis, researchers observed that PLAYFULGHOST is distributed via the BOOSTWAVE loader, which uses shellcode to inject malicious executables.
Targeted applications, such as Sogou, QQ, and 360 Safety, along with decoy files like LetsVPN, suggest a focus on Chinese-speaking Windows users. Notably, in July 2024, Canadian cybersecurity firm eSentire reported similar malicious campaigns leveraging fake Google Chrome installers to propagate Gh0st RAT.


