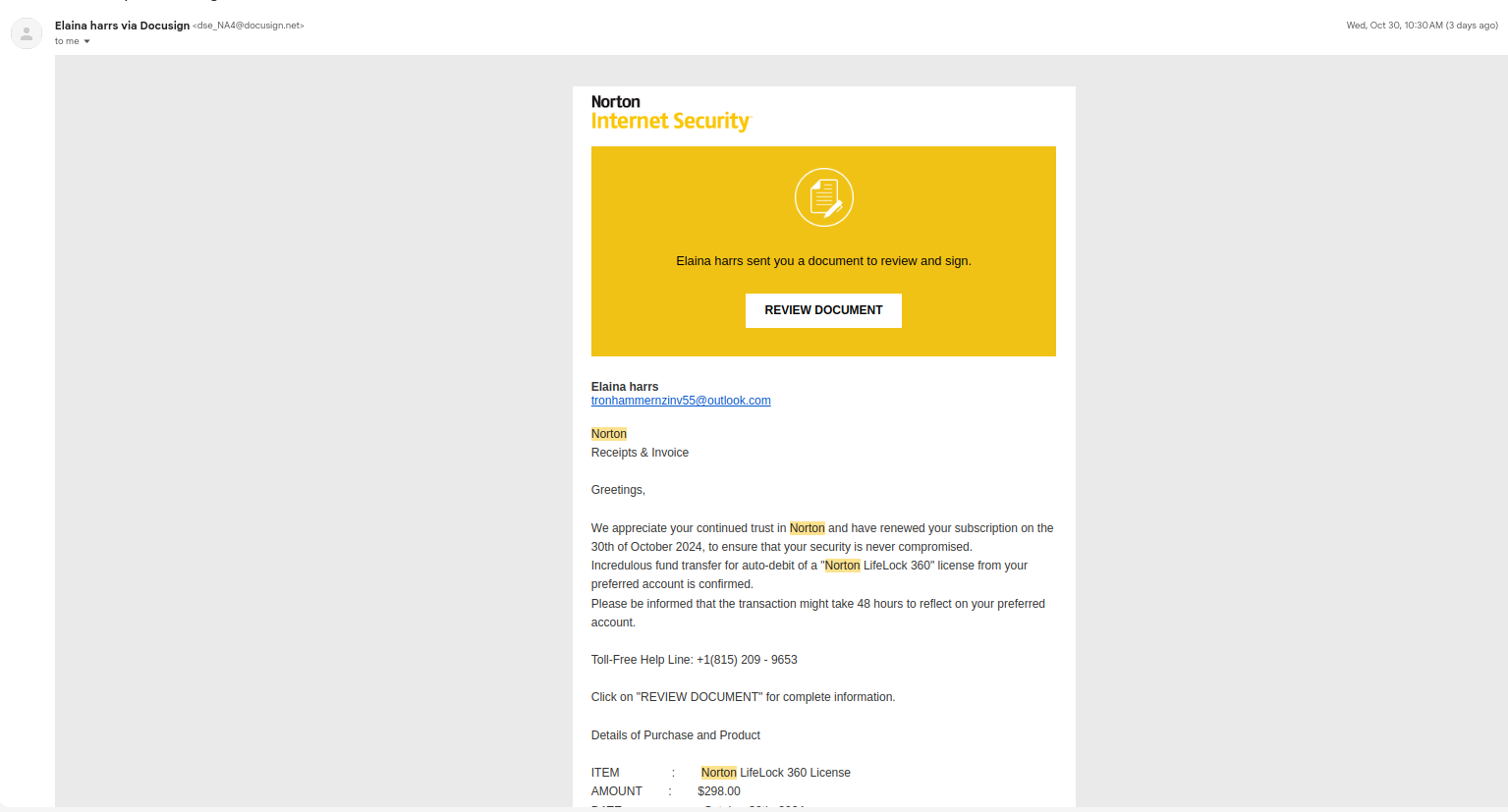
An actual fraudulent invoice sent via DocuSign, using Norton's branding and layout
DocuSign has found itself at the center of a new type of cyberattack: cybercriminals exploit its API to distribute counterfeit invoices that appear authentic. Unlike traditional phishing attacks involving fake links and emails, these incidents leverage legitimate DocuSign accounts and templates, making it more challenging for users and security systems to identify the threat.
The attackers create paid accounts on DocuSign, where they configure templates that mimic invoices from well-known brands, such as Norton Antivirus. These invoices include realistic details and often add extra fees, like a $50 “activation fee,” lending further credibility to the forgeries.
When a user signs such an invoice, they effectively authorize payment, which the attackers can then transfer to their accounts. These invoices are difficult to trace—they are sent directly through the DocuSign platform without malicious links or attachments, allowing them to bypass email filters.
In recent months, user complaints about such incidents on DocuSign forums have significantly increased. These attacks reveal that cybercriminals are increasingly using legitimate channels to mask their activities, complicating detection efforts.
Security experts at Wallarm have discovered that the attackers automate the process through DocuSign’s API, sending counterfeit invoices en masse with minimal manual input. Using the Envelopes API, they configure and dispatch thousands of invoices, fully customized to match company branding, such as Norton’s, creating the illusion of legitimate transactions.
Wallarm researchers emphasize that this threat is relevant for other e-signature services as well. To guard against such attacks, companies are advised to verify senders, implement internal approval protocols for financial transactions, and conduct employee training. Service providers must limit API request rates and deploy technologies to monitor suspicious activity.
This scheme marks a new chapter in cybercrime, where perpetrators embed their operations within trusted platforms, complicating detection. Organizations must enhance their defensive strategies, focusing particularly on API security and employee awareness.


