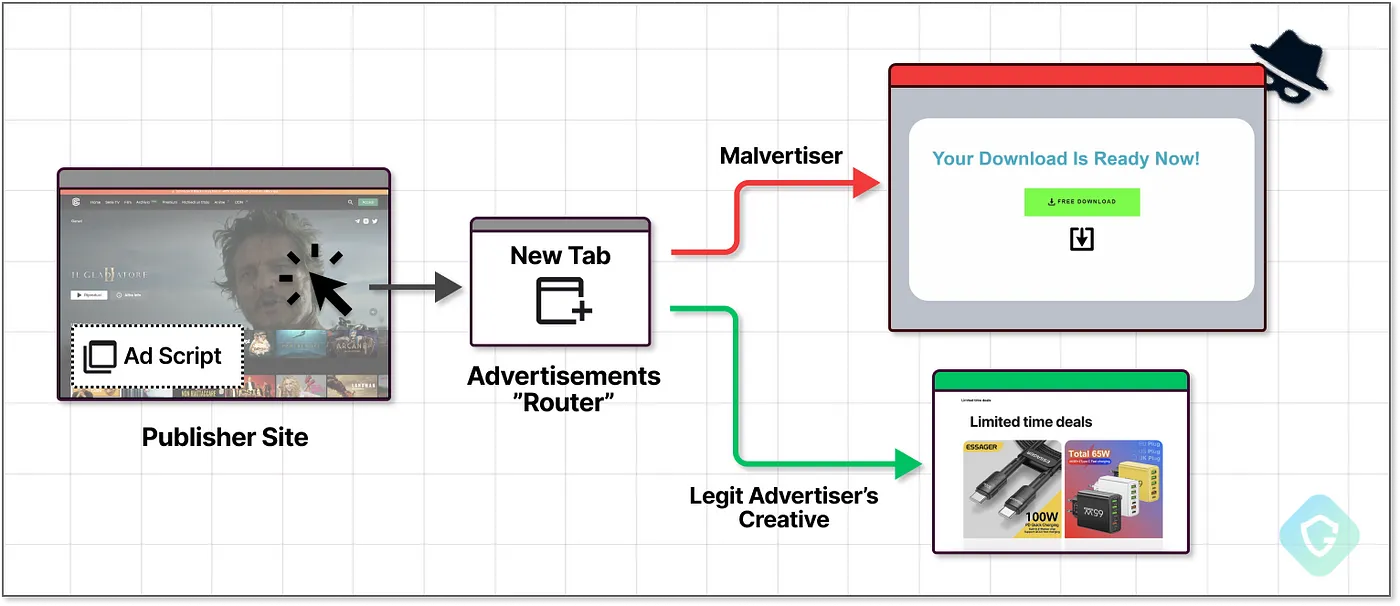
A visitor activating an ad-placement process and the ad network selecting the target creative
Cybersecurity experts at Guardio Labs have uncovered a new fraudulent campaign known as DeceptionAds, which exploits advertising networks to distribute malware. Over the past ten days, the attack has affected more than one million users, redirecting them to fake CAPTCHA pages.
The malicious campaign heavily relies on a single advertising network, Monetag, and drives traffic through more than 3,000 websites hosting pirated or clickbait content. Users are tricked into semi-automatically executing a Base64-encoded command, leading to the download of information-stealing malware such as Lumma.
In recent months, similar attacks have grown in scale, with multiple hacker groups adopting this method to distribute remote access trojans and post-exploitation tools. To obfuscate their malicious activities, the attackers have utilized the BeMob service.
The attack unfolds as follows: cybercriminals register with Monetag, after which traffic is redirected through a traffic distribution system (TDS) to CAPTCHA pages. These fake pages are hosted on platforms like Oracle Cloud, Cloudflare R2, and others.
Guardio Labs reported that Monetag has since removed over 200 accounts associated with the campaign following reports of violations. BeMob also disabled accounts used to disguise malicious links. Nevertheless, signs of the campaign’s resurgence were observed again on December 5.
The research highlights how advertising networks, designed for legitimate purposes, can be weaponized to facilitate cyberattacks. The issue is exacerbated by the unclear delineation of responsibility among advertising platforms, website owners, and hosting providers.
Such incidents underscore the urgent need for stricter oversight and moderation of advertising content to mitigate these risks.