Since the closure of the infamous Silk Road, the dark web has witnessed the emergence of numerous new marketplaces. Most of these platforms have an average lifespan of roughly eight months before succumbing to law enforcement actions or the fraudulent schemes of their administrators. Despite this, the realm of such platforms has undergone a significant evolution in terms of security.
One modern marketplace, operational since May 2020, showcases a groundbreaking approach to user protection. The platform has entirely abandoned the use of JavaScript—a popular but potentially vulnerable technology that can expose users to tracking risks even on the Tor network.
To guard against phishing, the platform has implemented a multi-layered security system. Among its standout features is a unique CAPTCHA mechanism that operates without JavaScript. This system relies on the browser’s <input type="image"> functionality, transmitting click coordinates to the server as request parameters (e.g., ?x=32&y=46). Users are required to perform specific actions to verify they are not bots. This innovation not only thwarts automated attacks but also raises users’ awareness of security measures.
The authentication process incorporates two-factor authentication based on PGP keys. During account creation, users upload a public key, which is used for signing messages. Accessing the account requires decrypting a message with a private key, ensuring a high level of security while educating users on encryption fundamentals.
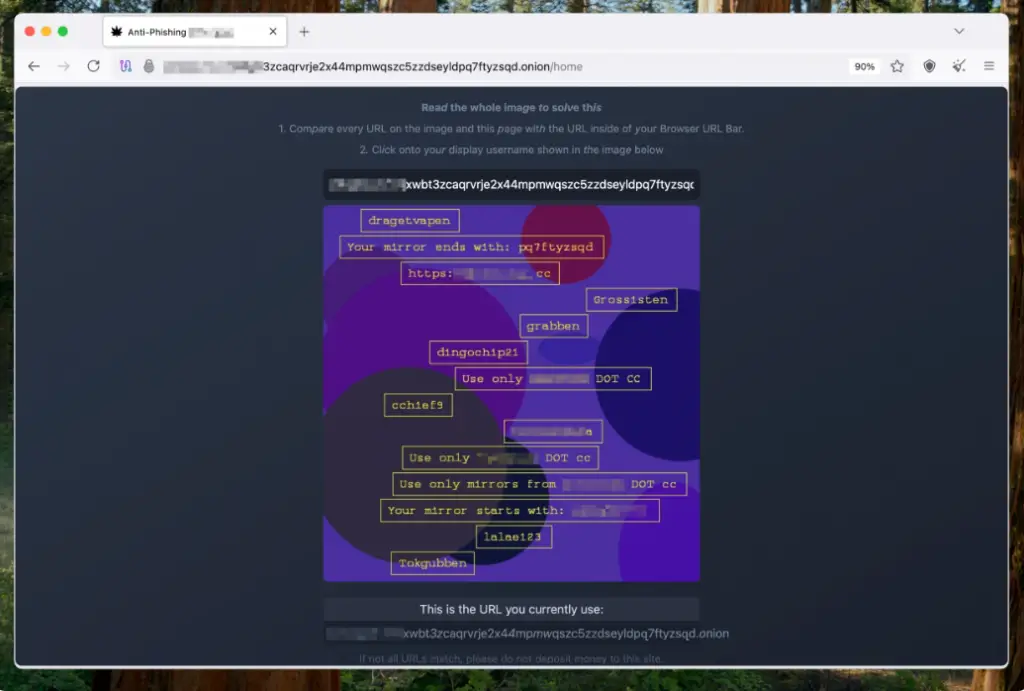
To enhance protection, the platform employs a tiered mirror system. Public URLs are accessible to all users, but registered users are assigned personalized URLs from a secured pool. As user activity progresses—for instance, through completing transactions—they gain access to even more secure mirrors. This approach, known as “Defense in Depth,” mitigates the risk of compromising the entire system.
Rather than relying on the popular Bitcoin cryptocurrency, the marketplace utilizes Monero, which provides superior anonymity. The Monero network conceals sender and receiver addresses, transaction amounts, and operational histories through advanced cryptographic algorithms, making it a preferred choice for such platforms.
The platform’s built-in cryptocurrency wallet serves as an escrow service. To minimize risks, a system has been developed that allows users to deposit funds three hours after placing an order, while sellers can automatically withdraw funds. This method maintains a minimal balance within the system, reducing the likelihood of fraudulent schemes.
The platform’s interface is crafted without JavaScript, requiring innovative design solutions. Side navigation utilizes radio buttons, and pop-up windows function through CSS identifiers. These techniques eliminate the need for scripts, thereby mitigating potential vulnerabilities. The service is believed to operate on Ruby, eschewing the Ruby on Rails framework, with its design powered by the CSS framework Tailwind.
Many of the platform’s technical innovations could find valuable applications in legitimate e-commerce sectors, particularly in areas concerning data protection and anti-phishing measures.


