Security researchers have uncovered a new cyberattack aimed at manipulating search engine results (SEO). The campaign, dubbed DragonRank, has impacted several countries in Asia and Europe, including Thailand, India, Korea, Belgium, the Netherlands, and China. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to compromise servers and deploy malicious software.
Experts from Cisco Talos reported that the attacks begin with the compromise of web applications such as phpMyAdmin and WordPress. The attackers inject malware, including BadIIS, by leveraging system vulnerabilities. As a result, the compromised servers are transformed into platforms for fraudulent operations related to SEO manipulation.
BadIIS allows attackers to modify website content to influence search engine algorithms. This facilitates the promotion of third-party websites, driving traffic to fraudulent resources and improving their ranking in search results. The primary objective is to fabricate search rankings to boost the visibility of certain websites, including those featuring adult content.
One of the distinguishing features of this campaign is its use of malware to bypass security mechanisms. For instance, BadIIS can masquerade as Googlebot, enabling it to interact stealthily with command-and-control (C2) servers, evading detection.
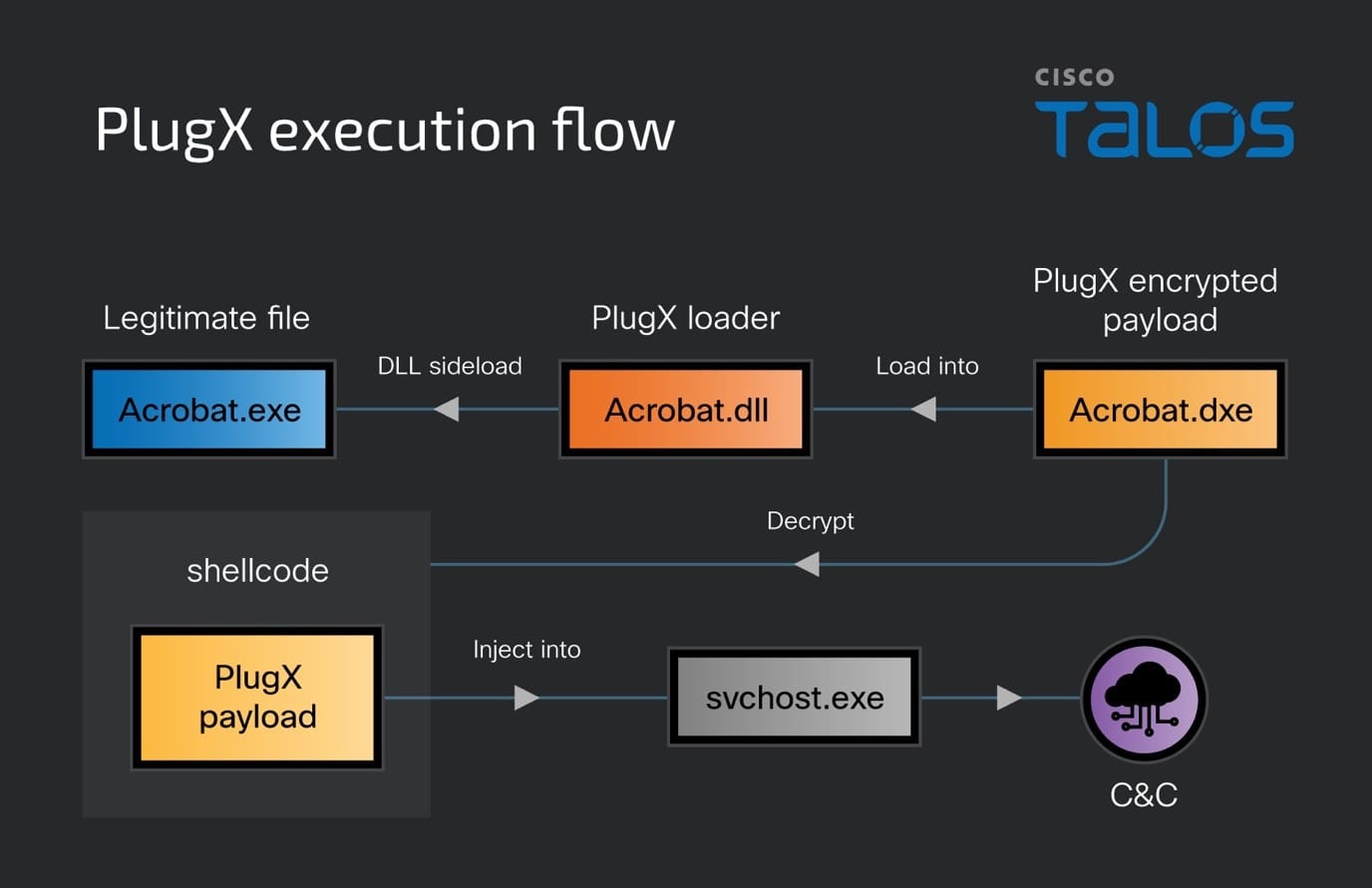
The DragonRank attacks span a wide range of industries, including jewelry, media, healthcare, transportation, and even feng shui organizations. The attackers actively employ credential-stealing tools and software such as Mimikatz and PlugX to maintain control over compromised systems.
Analysts also noted that the attackers provide their clients with detailed promotion plans, allowing them to select keywords and target markets to optimize their fraudulent websites. The hackers actively communicate with clients via messaging platforms such as Telegram and QQ, offering services to promote websites in specific languages and countries.
Experts urge companies to remain vigilant and monitor the security of their web applications, as such campaigns are becoming increasingly sophisticated and targeting vulnerable services.