At the end of May, experts from the Natto Team investigated the reconnaissance methods and toolkit of the APT41 hacker group, which is linked to Chinese cyber threats. Continuing their research, the specialists released a new report detailing several other Chinese groups employing similar techniques and tools.
Over the past decade, at least three Chinese hacker groups, including APT10, GALLIUM, and Stately Taurus, have utilized NBTscan or its modified version. This tool, designed for gathering information about systems within a network, enables the scanning of IP addresses and the retrieval of data such as usernames, computer names, and MAC addresses.
APT10, associated with China’s Ministry of State Security, employed NBTscan during the Cloud Hopper and Soft Cell operations to identify valuable services on network devices. According to Microsoft, the GALLIUM group used this tool to target global telecommunications providers in 2019. The infamous Mustang Panda, active in Southeast Asia, also utilized NBTscan to scan and analyze the networks of their victims.
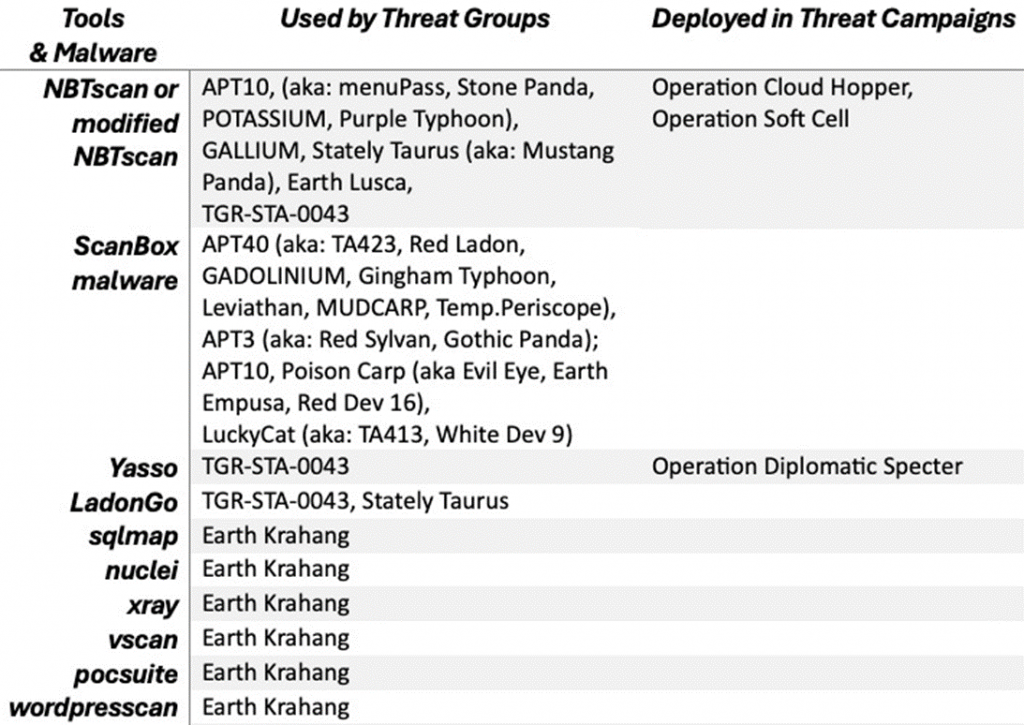
APT40, active since 2009, employs the malicious tool ScanBox, which allows data collection from infected systems without requiring software installation. This framework, written in JavaScript, gathers information about the user’s system, including the operating system, browsers, antivirus software, and other applications. ScanBox can also log keystrokes, making it a dangerous tool for stealing passwords and other confidential data.
In May 2024, researchers from Palo Alto Networks reported on the Diplomatic Specter campaign, which targeted government entities in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. As part of this campaign, the Chinese group TGR-STA-0043 utilized the LadonGo and Yasso tools. Yasso, a new toolkit that emerged in 2022, includes features for SQL penetration, scanning, and command execution. Yasso’s developer is a Chinese security expert known online by the alias SaiRson.
In addition to well-known tools, Chinese hackers are actively using various open-source solutions. For instance, the Earth Krahang group frequently employs tools like sqlmap and nuclei to search for vulnerabilities in servers. Some of these tools were developed by Chinese programmers.
A comprehensive list of hacker tools actively used by various Chinese cyber groups can be found in the image below:
Researchers note that the use of scanning tools, both well-known and open-source, remains one of the key strategies for Chinese hackers to identify vulnerabilities and launch subsequent attacks. This underscores the necessity of a comprehensive approach to safeguarding information systems, one that includes not only technical measures but also international collaboration in the realm of cybersecurity.
The situation also highlights the importance of continuous education and vigilance regarding new cyberattack methods for all participants in the digital space.