A critical vulnerability has been discovered in the popular WordPress plugin, GiveWP, which is widely used for collecting donations and conducting fundraising campaigns. This flaw endangers the security of over 100,000 websites, exposing them to the risk of remote code execution.
With the highest possible CVSS score of 10, the vulnerability identified as CVE-2024-5932 affects all versions of the plugin up to version 3.14.2, released on August 7, 2024. The issue was reported by a security researcher known by the pseudonym villu164.
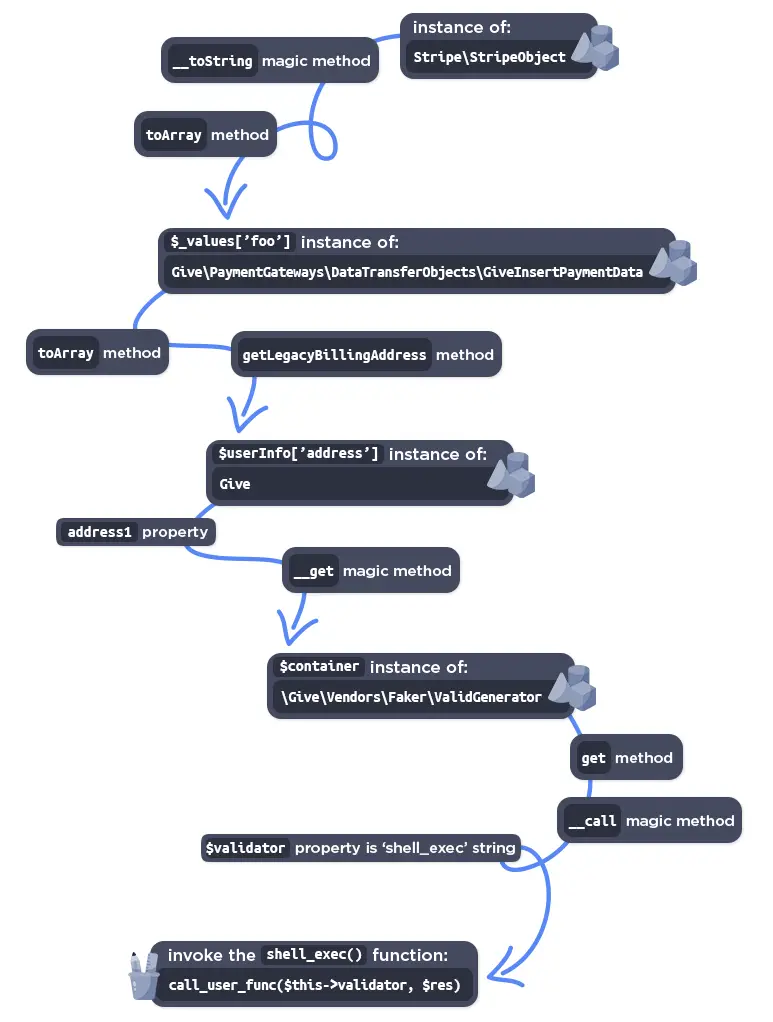
According to Wordfence, the GiveWP plugin is vulnerable to a PHP Object Injection attack via the “give_title” parameter. This vulnerability allows unauthorized attackers to inject a PHP object, which, when combined with a POP chain, enables remote code execution and the deletion of arbitrary files on the server.
The root of the problem lies in the “give_process_donation_form()” function, which is responsible for validating and sanitizing data entered into the donation form before passing it to the payment gateway. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow attackers to execute malicious code on the server, making it imperative to update the plugin to the latest version.
This news comes on the heels of another recently discovered critical vulnerability in the InPost PL and InPost for WooCommerce plugins (CVE-2024-6500), which also received the highest CVSS score and allows remote reading and deletion of arbitrary files, including wp-config.php. On Linux systems, only files within the WordPress directory are subject to deletion; however, attackers can read any files on the system. The issue was resolved in version 1.4.5 of the plugin.
Another serious vulnerability was identified by Wordfence researchers in the JS Help Desk plugin, installed on more than 5,000 sites. It has been assigned CVE-2024-7094 with a score of 9.8, allowing remote code execution through PHP injection. The fix was released in version 2.8.7.
Experts strongly recommend updating all vulnerable plugins to their latest versions to prevent potential attacks. Specifically, these vulnerabilities could be exploited to inject skimmers that steal financial information entered by website visitors.
Researchers also caution WordPress site owners against using unlicensed plugins and themes, as they can be a source of malware and other security threats. Ultimately, using legitimate software is the cornerstone of responsible website management. Security compromises for short-term gains are unacceptable.


