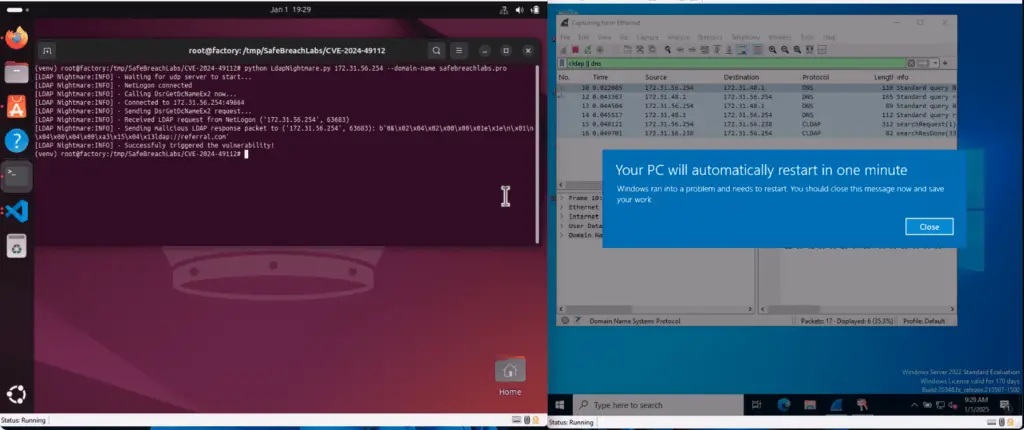
A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for a vulnerability in the Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), patched in December 2024, was recently published online. The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-49113 (CVSS 7.5), could result in a denial-of-service (DoS) attack. Its resolution was part of Microsoft’s December security updates, which also addressed CVE-2024-49112 (CVSS 9.8), a critical integer overflow vulnerability enabling remote code execution.
Both vulnerabilities were discovered by independent researcher Yuki Chen (@guhe120). The PoC exploit, dubbed “LDAPNightmare” by researchers at SafeBreach Labs, can crash a Windows server with no preconditions if the domain controller’s (DC) DNS server is accessible from the internet.
The attack leverages a DCE/RPC request sent to the target server, causing the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) to fail and forcing the system to reboot. The exploitation process relies on a crafted CLDAP packet, wherein the “lm_referral” value is set to a non-zero state.
Even more concerning is the potential for this exploit chain to be adapted for remote code execution by modifying the parameters of the CLDAP packet.
In its advisory, Microsoft confirmed that CVE-2024-49112 can be exploited via RPC requests from untrusted networks to execute arbitrary code within the context of the LDAP service. Successful exploitation requires sending a specially crafted RPC request that triggers the domain controller to interact with the attacker’s domain.
To mitigate potential threats, Microsoft strongly recommends installing the December security updates. For organizations unable to update immediately, it is advised to implement monitoring for suspicious CLDAP responses, DsrGetDcNameEx2 requests, and DNS SRV queries.


