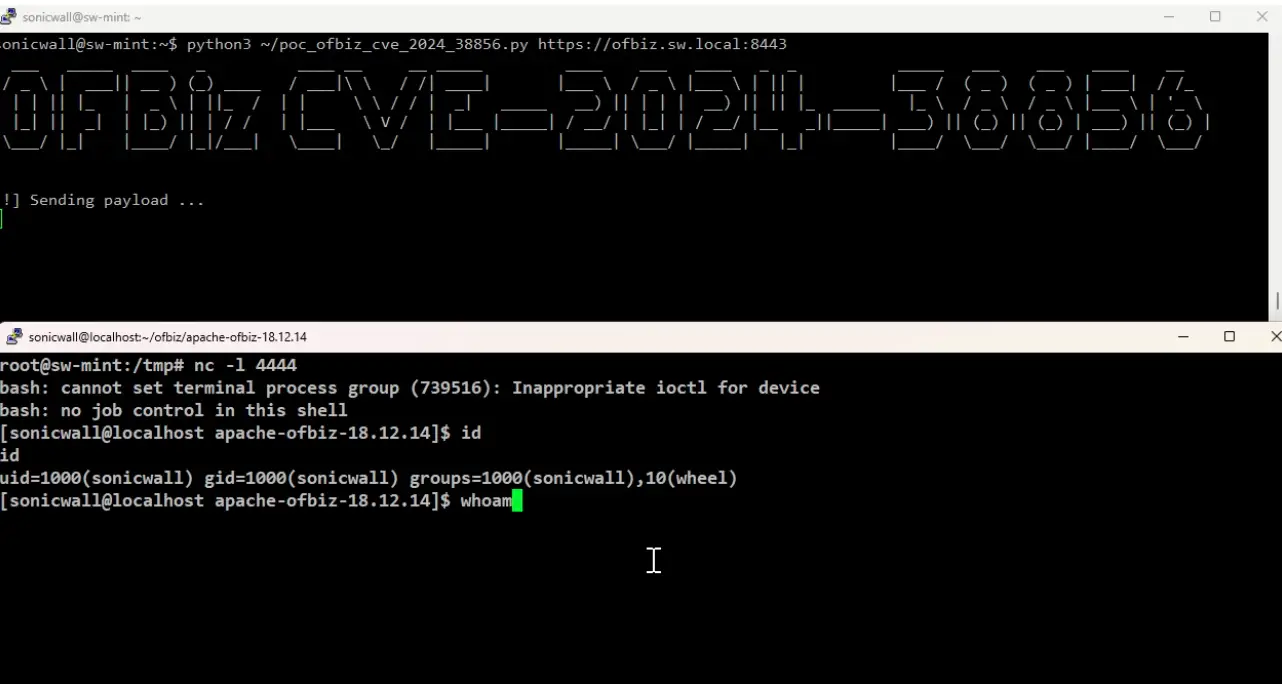
A new vulnerability has been discovered in Apache OFBiz, allowing attackers to remotely execute code on vulnerable instances of the software. Known as CVE-2024-38856, this issue has been assigned a CVSS score of 9.8, indicating its critical severity. Vulnerable instances include versions of Apache OFBiz released before version 18.12.15.
SonicWall, the company that identified and reported the vulnerability, noted that the root cause lies in the authentication mechanism. This flaw permits unauthorized users to access functions that typically require login, thereby paving the way for remote code execution.
CVE-2024-38856 also serves as a bypass for the patch addressing CVE-2024-36104, which was resolved in June 2024 with the release of version 18.12.14. According to SonicWall representatives, the issue stems from the Override View function, which exposes critical endpoints to unauthorized users, enabling them to execute remote code via specially crafted requests.
Security researcher Hasib Vora pointed out that access to the ProgramExport endpoint was provided without authentication, allowing attackers to exploit any other endpoint not requiring authorization through the Override View function. Fortunately, the vulnerability was patched in OFBiz version 18.12.15 with this commit on GitHub.
While neither Apache representatives nor SonicWall researchers provided clear information on whether the vulnerability had been exploited prior to discovery, they have classified it as a zero-day flaw. This designation underscores the urgency for users to update to the secure version as soon as possible, given that hackers are already aware of how to exploit the vulnerability in real-world attacks.
These events coincide with another critical vulnerability in OFBiz, CVE-2024-32113, which is already being actively exploited to deploy the Mirai botnet. Although a patch for this vulnerability was released in May 2024, administrators have been slow to implement updates, leaving their infrastructure exposed.
In December 2023, SonicWall also reported another zero-day vulnerability in the same software (CVE-2023-51467), which allowed for bypassing authentication protections. This vulnerability similarly faced numerous exploitation attempts by malicious actors.


