The ScarCruft group from North Korea has once again exploited a vulnerability in Windows to distribute the RokRAT malware. The exploitation targets CVE-2024-38178, a memory corruption vulnerability in the Scripting Engine, rated with a CVSS score of 7.5, which allows remote code execution via Edge in Internet Explorer mode.
Microsoft released a patch for this issue as part of the August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, but the hackers continue to aggressively target unpatched systems.
To initiate the attack, the adversaries must persuade the victim to click on a specially crafted link. Researchers from ASEC and the National Cyber Security Centre of South Korea (NCSC) have dubbed the campaign “Operation Code on Toast.” Internationally, the ScarCruft group is also known as TA-RedAnt, APT37, InkySquid, Reaper, Ricochet Chollima, and Ruby Sleet.
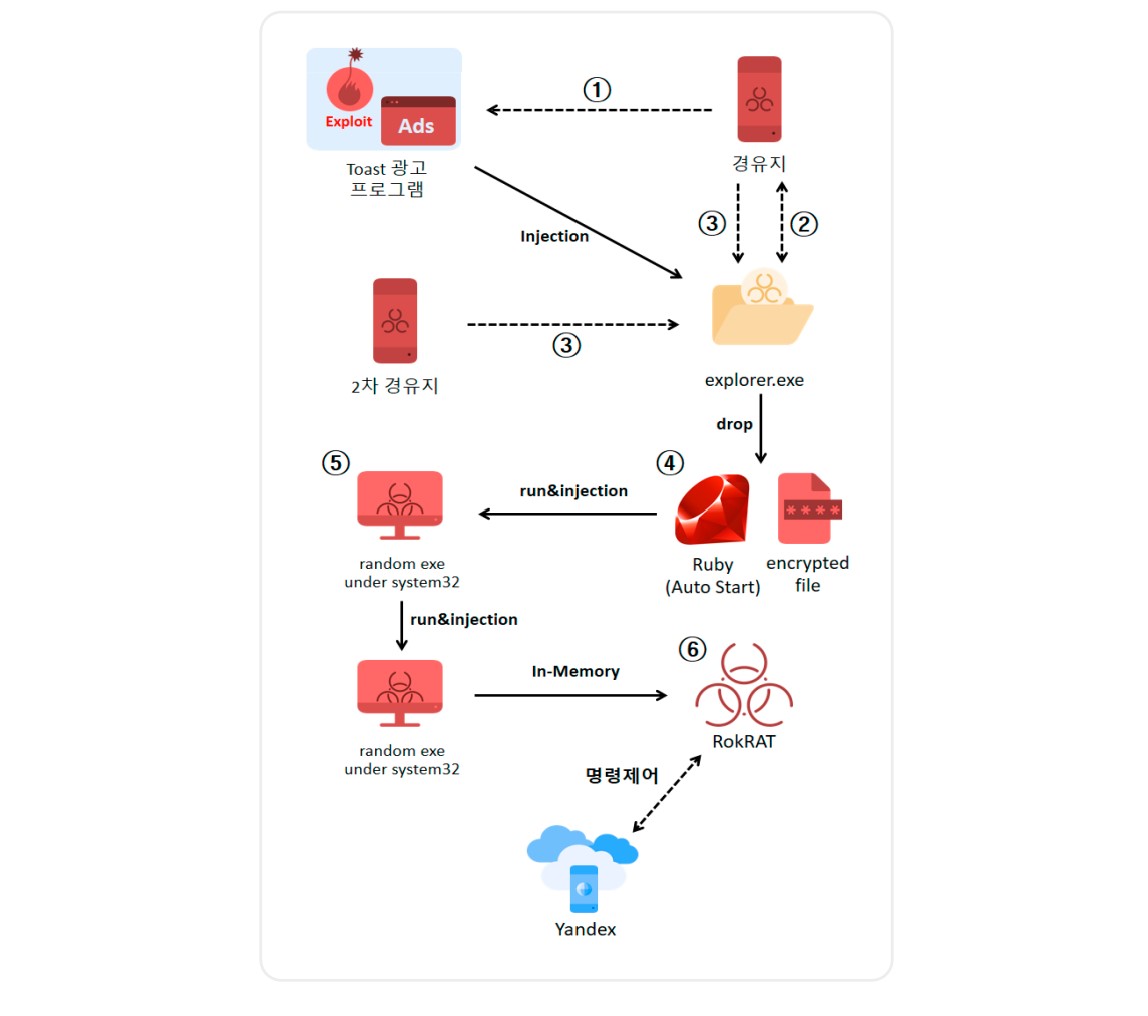
A distinctive feature of this attack is the use of “toast” notifications—pop-ups that appear at the bottom of the screen. The attackers compromised the server of an unnamed advertising agency that provides content for such notifications and injected malicious code into the ad script.
The vulnerability was triggered when the malicious content was loaded via a “toast” notification that leveraged the outdated Internet Explorer module. This caused a type confusion error in the JavaScript Engine (jscript9.dll), allowing the attackers to infiltrate systems with the vulnerable software and gain remote access.
The updated version of RokRAT can manage files, terminate processes, execute commands from a remote server, and collect data from popular applications like KakaoTalk and WeChat, as well as from browsers such as Chrome, Edge, Opera, and Firefox. To orchestrate their attacks, RokRAT utilizes legitimate cloud services, including Dropbox, Google Cloud, and Yandex Cloud, to disguise its activities.
ScarCruft has a history of exploiting vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer. Previous attacks attributed to them involved CVE-2020-1380 and CVE-2022-41128. Experts emphasize that North Korean hackers continue to refine their methods and exploit various vulnerabilities. It is recommended to regularly update operating systems and software to protect against such attacks.