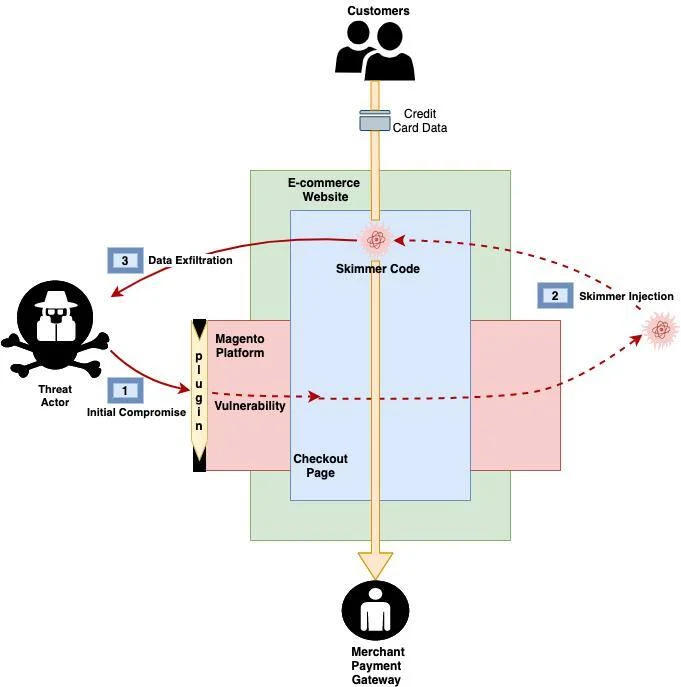
A typical Magecart attack flow
According to a recent Trustwave report, hackers have intensified their attacks on e-commerce websites ahead of the holiday season, targeting credit card data and personal information. Magecart attacks, which first emerged in 2015, remain one of the most significant threats to online store owners.
Magecart continues to thrive due to the widespread use of the Magento platform, which underpins thousands of online stores worldwide. The threat was exacerbated by the 2020 pandemic, as the shift to online shopping expanded the attack surface.
Hackers employ a variety of methods to gain unauthorized access to websites. They exploit vulnerabilities in platforms, third-party services, or site infrastructure. In 2024, cybercriminals actively leveraged the following vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2024-20720 (CVSS score: 9.1): A critical flaw in Magento allowing the execution of arbitrary system commands. Attacks exploiting this vulnerability began in April 2024, leading to widespread website breaches.
- CosmicSting (CVE-2024-34102 and CVE-2024-2961): These vulnerabilities enabled attackers to access sensitive data, execute remote code, and inject malicious scripts. The campaign impacted up to 75% of Adobe Commerce and Magento platforms.
Once access is gained, hackers embed skimmers on critical pages, particularly checkout pages. These scripts collect user data, including card numbers and CVV codes.
In 2024, there was a notable increase in abuse of the popular Google Tag Manager (GTM) tool, used by administrators for content management. Hackers create their own GTM accounts to inject malicious scripts, which are then executed on compromised sites. This method is harder to detect as GTM appears legitimate.
The stolen data is exfiltrated to attacker-controlled servers using various methods, including HTTP requests and WebSocket connections. To complicate analysis, the data is often encoded in Base64.
To mitigate the risks posed by Magecart attacks, the following measures are recommended:
- Regularly update platforms and extensions;
- Disable unnecessary components and third-party scripts;
- Configure a Content Security Policy (CSP) to restrict the execution of unauthorized scripts;
- Implement Subresource Integrity (SRI) to verify the integrity of downloaded resources;
- Conduct regular monitoring of file changes and external connections.
Magecart attacks remain a formidable threat, necessitating a comprehensive and proactive approach to defense.