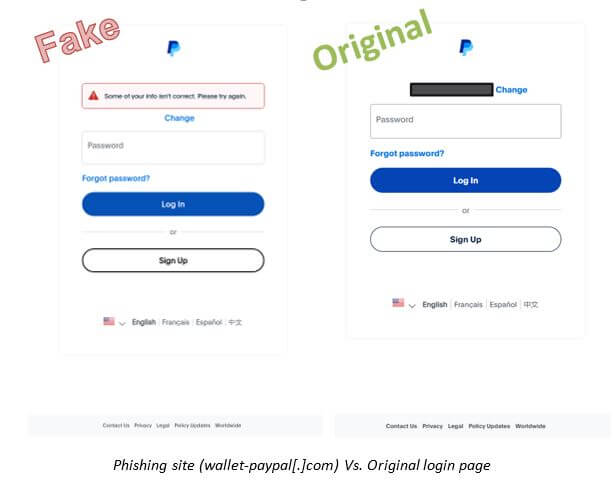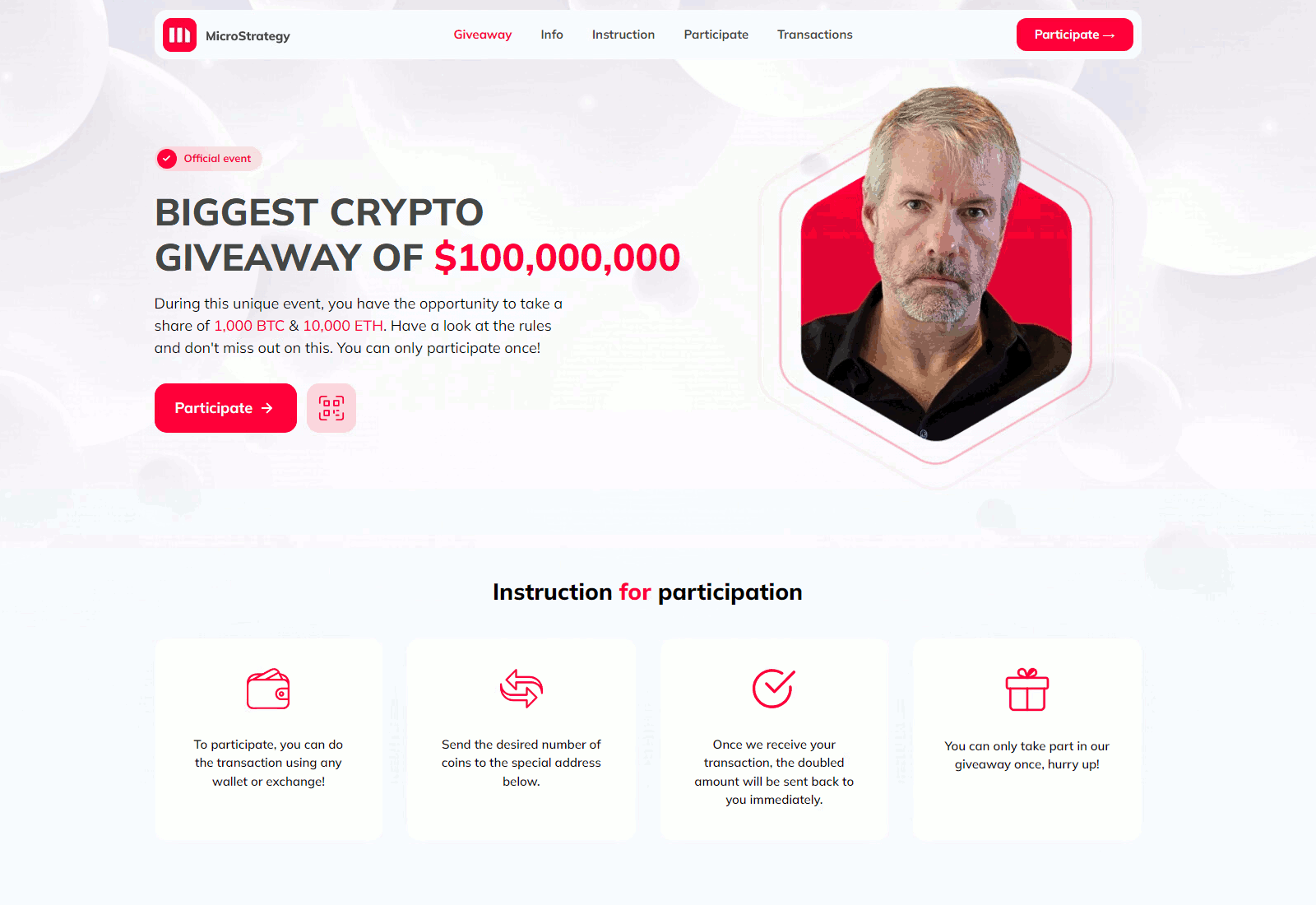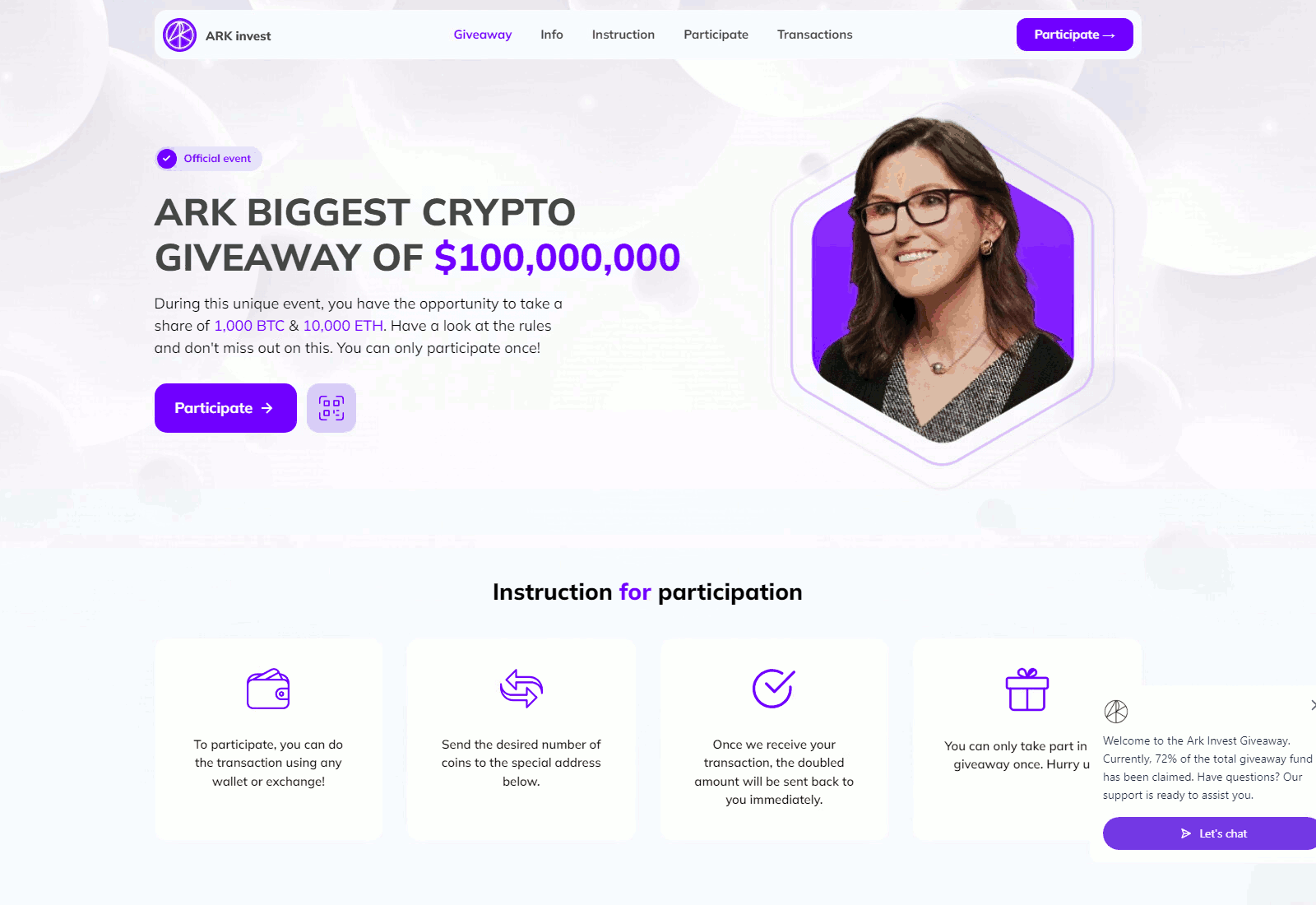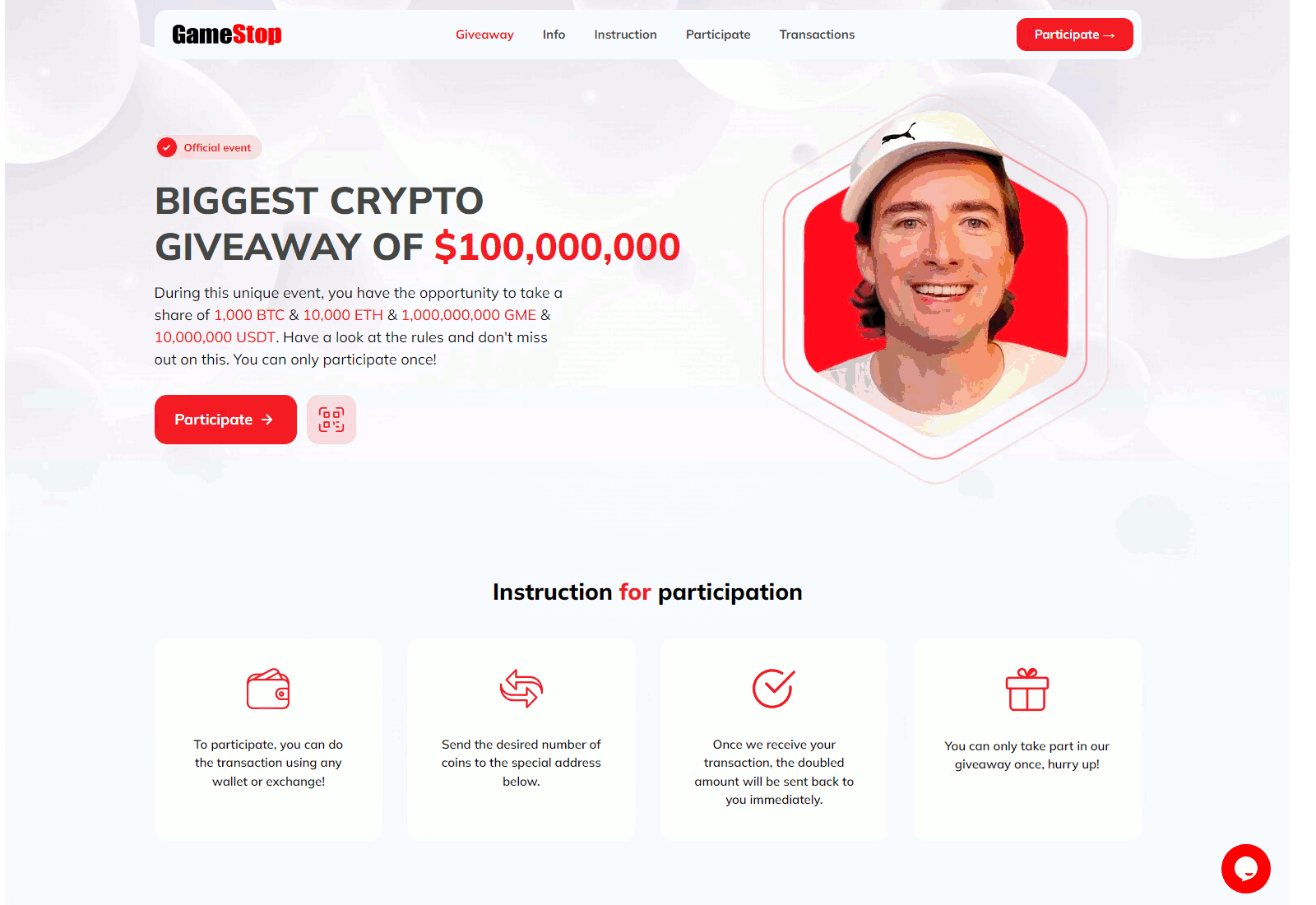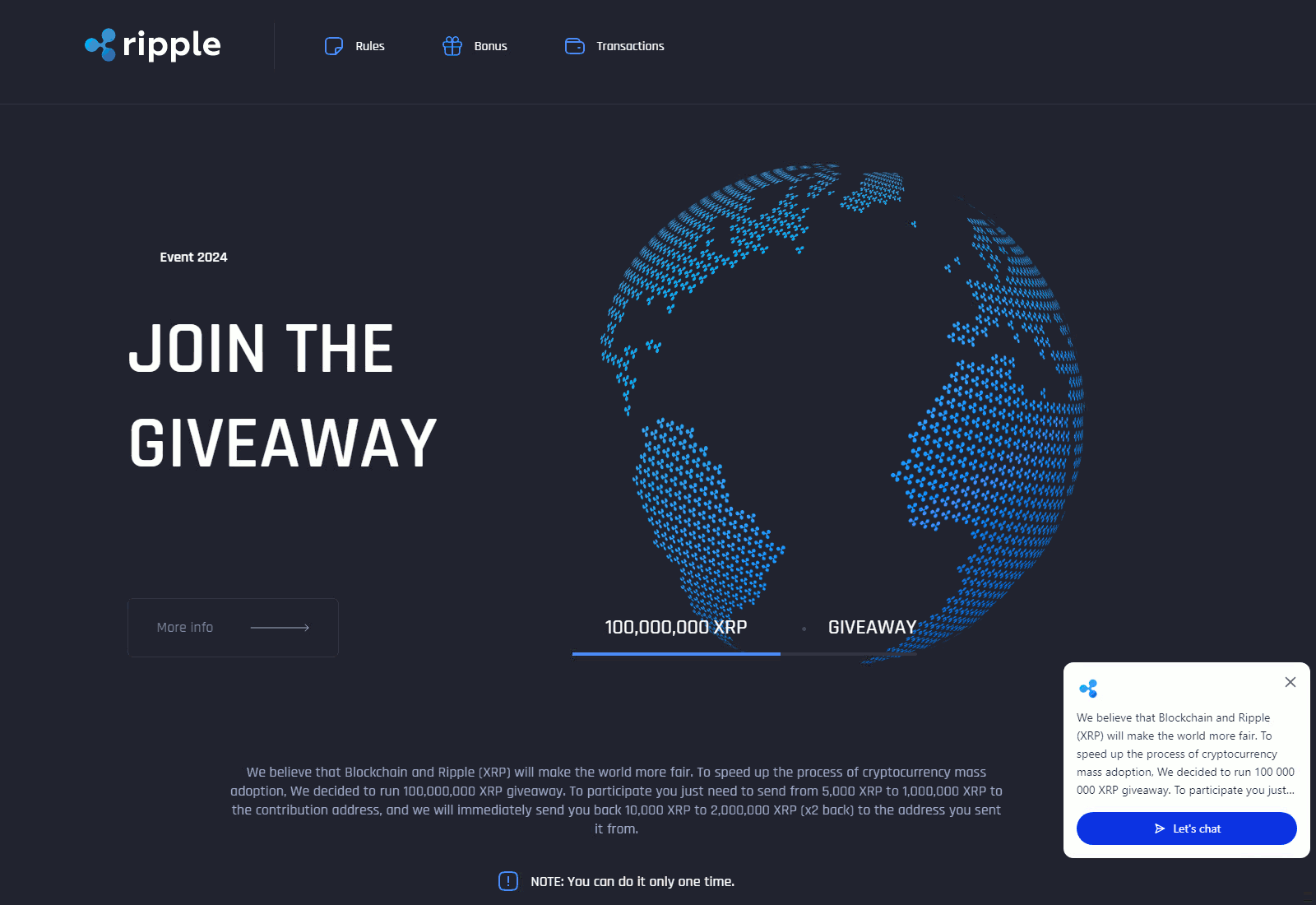
In the world of cryptocurrencies, where innovation and technology go hand in hand, a new threat has emerged for investors and users alike. Fraudsters, armed with advanced AI technologies and deepfakes, are crafting increasingly sophisticated scams, jeopardizing the security of digital assets for millions worldwide.
Among these cybercriminals, a group codenamed CryptoCore stands out with its cunning tactics and, unfortunately, its successful deception of numerous victims. Their arsenal is impressive: deepfake technology to create fake videos, hacked YouTube accounts with millions of subscribers, and professionally designed websites. Together, these tools create a convincing illusion of legitimacy, luring users into voluntarily sending their cryptocurrencies to the scammers’ wallets.
CryptoCore’s modus operandi is rooted in exploiting human trust in well-known brands, celebrities, and significant events. The attackers skillfully disguise their messages as official communications from trusted sources, be it social media accounts or pages of popular events. This tactic allows them to parasitize the reputations of respected figures and organizations, deceiving even the most cautious users.
Their scam mechanism is refined to the last detail. The victim is usually redirected to a carefully crafted fake site, promising quick and easy profits. To amplify the effect and create a sense of urgency, the fraudsters often use time-limited “exclusive” offers. The potential victim is led to believe that if they do not act immediately, they will miss a unique opportunity to earn.
CryptoCore’s success is based on three key factors: meticulous preparation before each “operation,” a sophisticated technical infrastructure, and the ability to rapidly disseminate fraudulent materials to a vast audience through popular social platforms.
The preparation process for an attack includes several stages. First, the attackers hack accounts with a large number of subscribers, most often on YouTube. Their hacking methods range from sophisticated phishing campaigns to the use of malware distributed via email. Once access to an account is gained, the fraudsters meticulously prepare deepfake content, waiting for the right moment to release it.
On the day of the planned operation, the compromised account undergoes a complete transformation. The background image is changed, the channel description is updated, and fake content is added—all to enhance credibility. When users search for information about an official event, they are highly likely to encounter fake content, given the large subscriber base of the hacked account.
The scale of CryptoCore’s activities is staggering. Over a six-month research period, more than 1,200 cryptocurrency wallets used in fraudulent schemes were identified. The fraudsters most frequently dealt with cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, Tether, and Dogecoin. The total turnover of funds in these wallets amounted to approximately $5.4 million, underscoring the vast scale of the problem.
YouTube, being the world’s largest video-sharing platform with an audience in the billions, became the primary target of CryptoCore’s attacks. Analysis of the hacked accounts revealed that over 20% of them had more than a million subscribers. The largest share, about 36%, fell on accounts with an audience of 100,000 to 500,000 people. This choice is no coincidence—a large number of subscribers not only ensures wide reach but also adds a veneer of legitimacy to the fraudulent messages.
Deepfake technology has become a key tool in the fraudsters’ arsenal. To create convincing fakes, snippets of real speeches and interviews of well-known personalities are used. For example, to imitate content related to SpaceX and Elon Musk, the attackers used footage from events such as SpaceX All Hands 2024, the Starship Flight Test, and the 2022 Starship Update. In the case of Michael Saylor, founder of MicroStrategy, the fraudsters created fake videos with titles like “Bitcoin: The Digital Energy of the Future with Michael Saylor” or “10 Rules for Success in the Crypto World by Michael Saylor.”
Statistics collected from January to June 2024 revealed 340 different domains used to propagate CryptoCore’s fraudulent schemes. Analysis showed that the most frequently exploited themes were MicroStrategy, SpaceX, and Tesla—companies and brands closely associated with the world of cryptocurrencies and innovation.
The technical aspect of CryptoCore’s operations is impressive in its complexity. The scammers’ websites are built using obfuscated JavaScript scripts, making analysis and detection significantly more difficult. This approach effectively hides the addresses of cryptocurrency wallets, constants, and other critical elements, forming dynamically generated content. Wallet QR codes, often used to simplify the process of transferring funds, are generated by a separate obfuscated script and stored locally in the victim’s device memory.
A particularly worrying aspect is that the fraudsters actively redirect potential victims to mobile devices. Statistics show that the ratio of detected CryptoCore malicious activity on desktop computers to smartphones is 2:5. This trend is explained by the fact that mobile devices are often less protected against cyber threats, increasing the fraudsters’ chances of success.
Geographical analysis of CryptoCore’s attacks showed that the most vulnerable countries were the United States, the United Kingdom, Brazil, and Germany. The high level of cryptocurrency penetration and developed digital infrastructure in these countries make them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
In light of the growing threat from cryptocurrency fraudsters, users must exercise increased vigilance. It is important to remember that in the world of finance, there are no free lunches and offers that seem too attractive are most often scams. Extra caution should be taken when interacting with social media accounts that have a large number of followers but exhibit suspiciously low activity or inconsistent content.
Experts strongly recommend the installation of reliable antivirus software not only on computers but also on mobile devices. Regular updates of operating systems and applications, the use of strong and unique passwords, as well as two-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to fraudsters.
Combating cryptocurrency fraud requires a comprehensive approach, including both technical protection measures and raising user awareness. Only through joint efforts by IT companies, law enforcement agencies, and users themselves can a safe environment be created for the development of cryptocurrency technologies and protect investors from financial losses.