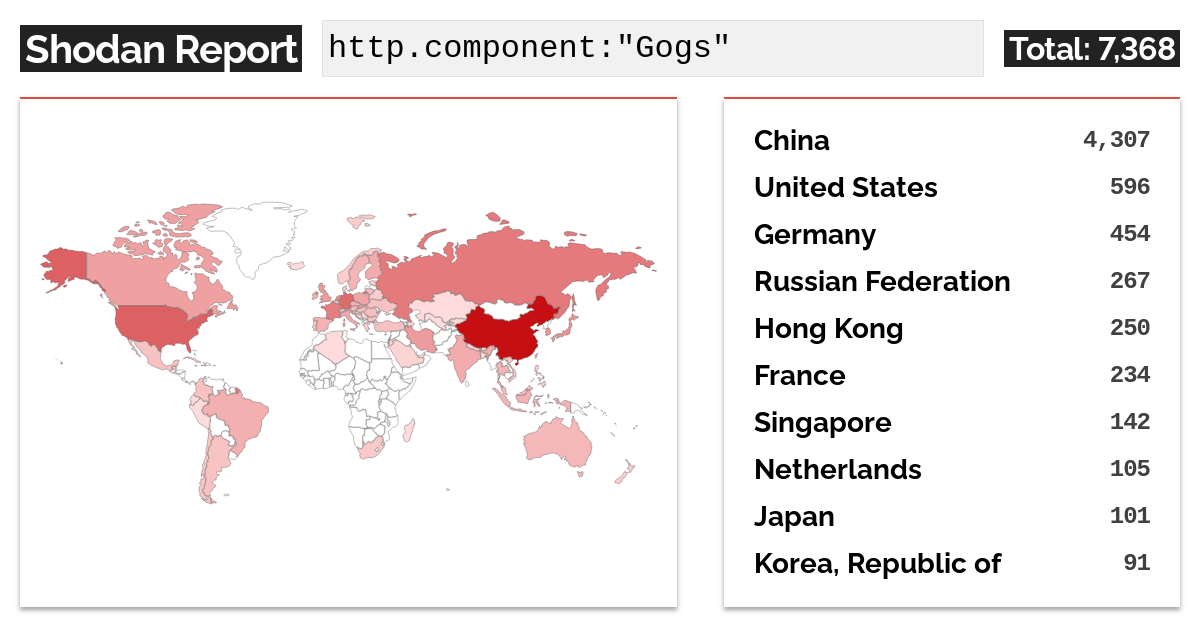
A quick Shodan search lists around 7300 open Gogs instances
In Gogs, a popular self-hosted open-source Git repository service, four unresolved vulnerabilities have been discovered, three of which are critical. These vulnerabilities could allow an authenticated attacker to compromise vulnerable instances, steal or destroy source code, and implant backdoors.
Thomas Chauchefoin, and Paul Gerste, researchers from SonarSource, highlighted the following vulnerabilities in their report:
- CVE-2024-39930 (CVSS 9.9) — Argument injection in the embedded SSH server.
- CVE-2024-39931 (CVSS 9.9) — Internal file deletion.
- CVE-2024-39932 (CVSS 9.9) — Argument injection in change previews.
- CVE-2024-39933 (CVSS 7.7) — Argument injection in the creation of new releases.
Exploiting the first three vulnerabilities allows for the execution of arbitrary commands on the Gogs server, while the fourth vulnerability permits reading arbitrary files, including source code and confidential settings.
To exploit all four vulnerabilities, the attacker must be authenticated on the target system. For CVE-2024-39930, it is also necessary that the embedded SSH server is enabled and a vulnerable version of the env binary is used. Additionally, the attacker must possess a valid private SSH key.
If registration in Gogs is enabled, an attacker can simply create a new account and register their own SSH key. Otherwise, they must compromise another account or steal a private SSH key from an existing user.
Instances of Gogs running on Windows and in Docker containers are not vulnerable to the described attacks. However, instances on Debian and Ubuntu are vulnerable due to the support of the “–split-string” option in the env binary.

According to Shodan, about 7,300 Gogs instances are accessible on the Internet, with nearly 60% located in China, followed by the USA, Germany, Russia, and Hong Kong. It remains unclear how many of these servers are vulnerable.
SonarSource experts also noted that the vulnerability was discovered over a year ago, but the maintainers of Gogs have not released patches and have effectively ceased communication with researchers after April 28, 2023, when they acknowledged receipt of the initial report.
In light of the lack of updates, users are advised to disable the embedded SSH server, prohibit user registration, and consider transitioning to Gitea. Additionally, SonarSource specialists have released a custom patch that Gogs users can apply to protect themselves.
This situation highlights that even popular developer tools can become targets of attacks if proper security measures are not taken, thereby jeopardizing software supply chains. It serves as a reminder for developers and administrators to continuously monitor and implement protective measures to prevent potential cyber threats.


