The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) servers, high-performance computing (HPC) applications, and AI in high-end smartphones has driven the sustained growth of the semiconductor industry, leading to a surge in demand. As Apple begins placing large orders at TSMC’s 3nm process node, more customers are following suit, which will significantly increase the revenue proportion. It is estimated that in 2024, the 3nm process node will account for more than 20% of TSMC’s revenue.
According to UDN, chip design companies such as Qualcomm, AMD, and Nvidia have begun placing orders at TSMC’s 3nm process node, ensuring capacity utilization. Orders are now queued up until 2026, and even with TSMC doubling its capacity compared to last year, it remains insufficient. With customers rushing to secure capacity, TSMC’s 3nm capacity will face tight supply over the next two years, excluding Intel’s potential CPU outsourcing demand.
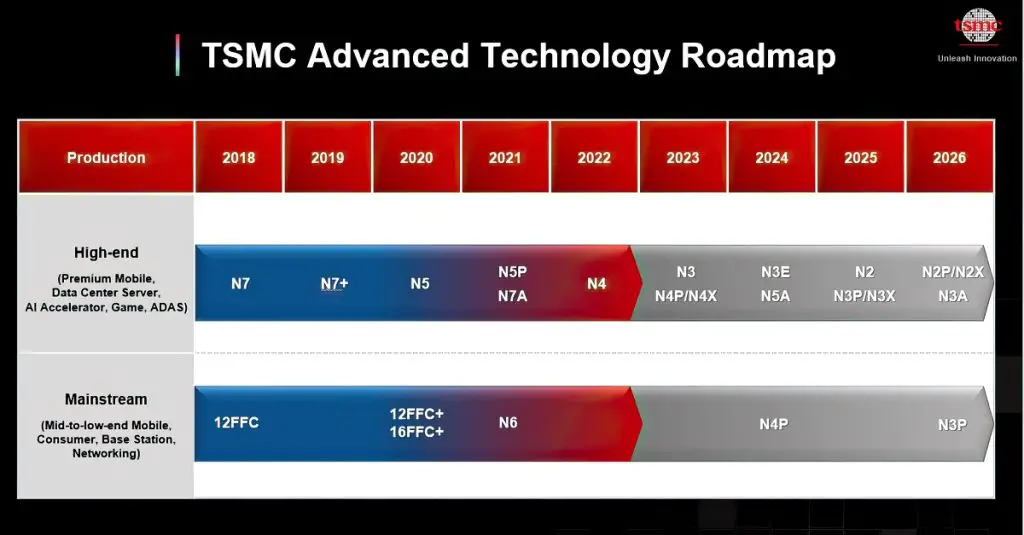
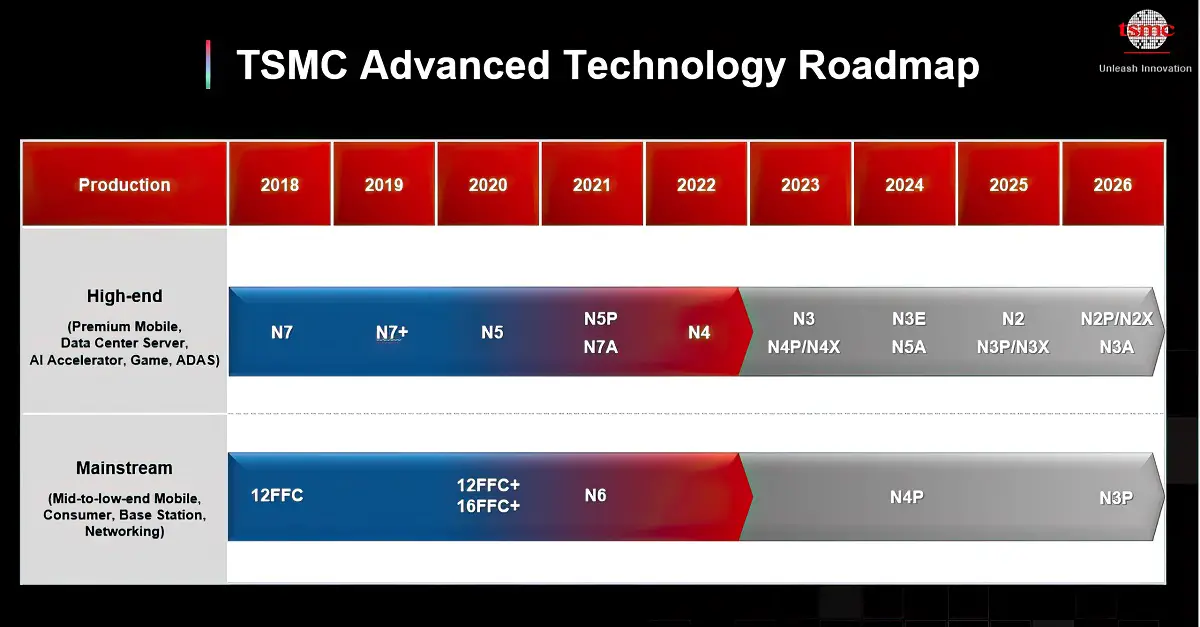
TSMC’s 3nm process node offers a variety of technologies, including N3, N3E, N3P, N3X, and N3A. With continuous upgrades in 3nm technology, the upcoming N3E will target AI accelerators, high-end smartphones, and data centers. N3P is expected to enter mass production in the second half of this year and become mainstream for mobile devices, consumer products, base stations, and network applications by 2026. N3X and N3A are specifically designed for high-performance computing and automotive customers.
To ensure stable supply over the next two years, TSMC has implemented several measures to expand capacity. During a previous earnings call, TSMC stated that due to the strong market demand for 3nm capacity, it would take various measures to address this, including converting some 5nm production line equipment to 3nm lines. Industry insiders predict that TSMC’s total 3nm capacity will continue to increase, with monthly production expected to reach 120,000 to 180,000 wafers.


