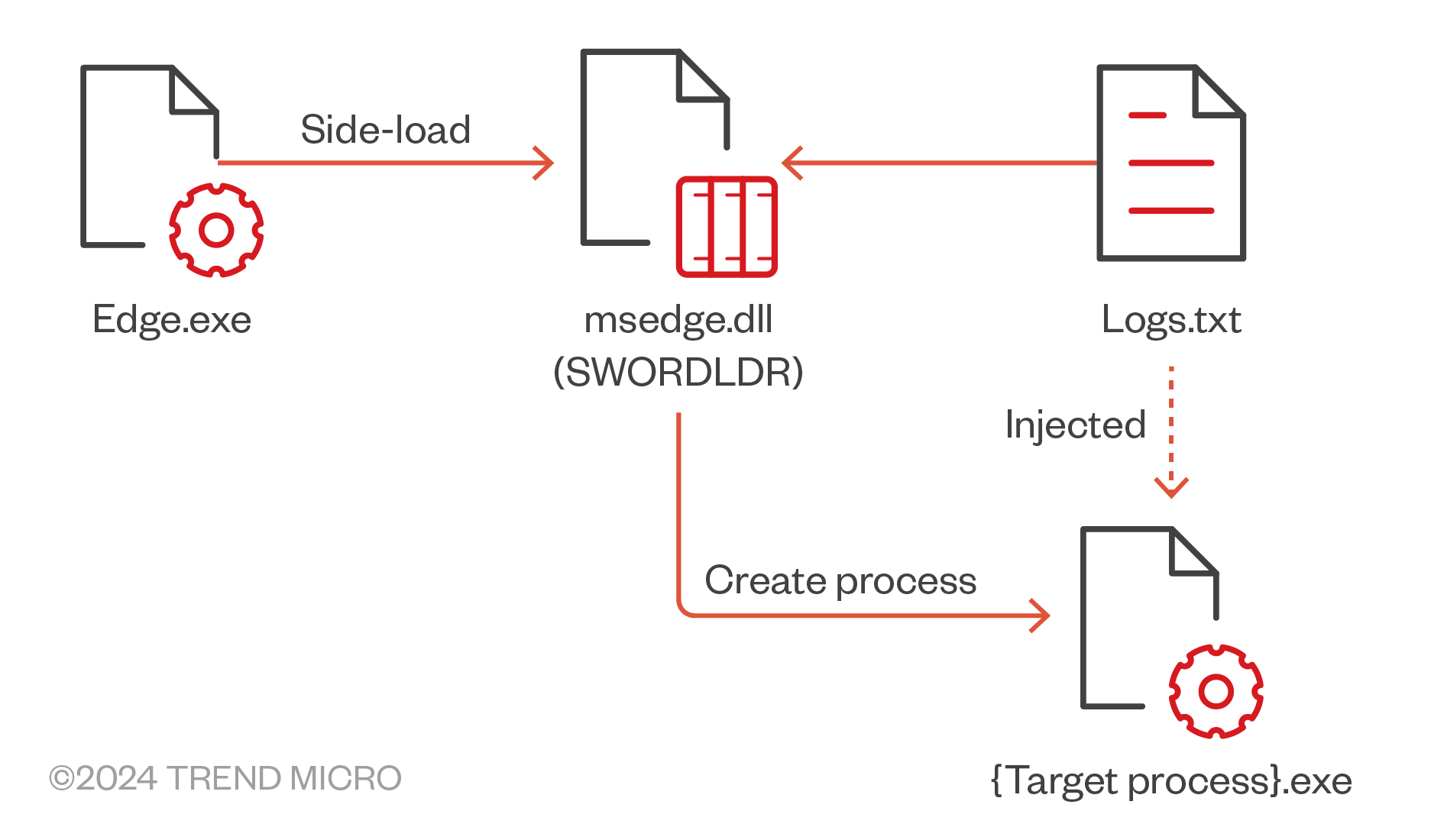
Execution flow of Cobalt Strike components
In July of this year, Trend Micro uncovered a cyberattack on Taiwanese government structures, allegedly linked to the Chinese group Earth Baxia. The attackers exploited a recently discovered vulnerability in GeoServer (CVE-2024-36401, CVSS: 9.8), enabling them to infiltrate systems not only in Taiwan but across other Asia-Pacific countries such as South Korea, Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines.
Trend Micro experts reported that the hackers employed phishing techniques using forged documents and letters to primarily target governmental institutions, telecommunications firms, and the energy sector. Notably, among the decoys found were documents written in simplified Chinese, suggesting a potential spread of the attack into China, though concrete information regarding this is yet to be confirmed.
The primary objective of these attacks was the deployment of Cobalt Strike malware and a previously unknown backdoor named EAGLEDOOR. This backdoor is used for data collection and the delivery of additional malicious components. The attackers employed GrimResource and AppDomainManager techniques to load and execute malicious software on compromised devices, masking their activities with fake files embedded in ZIP archives.
Particularly striking is the fact that the Japanese company NTT Security Holdings had earlier detected similar attacks using the same methods against targets in Taiwan, the Philippines, and Vietnam, hinting at a connection between Earth Baxia and the notorious APT41 group.
To manage the compromised systems, the attackers utilized domains mimicking popular cloud services such as Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure. The operations were accompanied by data transmission through multiple protocols, including DNS, HTTP, and Telegram, underscoring the attackers’ high level of sophistication.
According to researchers, the campaign’s goal was the prolonged compromise of infrastructures, followed by data exfiltration. This incident vividly illustrates that cybersecurity in the modern world transcends individual nations. Only through close international collaboration and continuous enhancement of defense measures can such sophisticated and large-scale threats be effectively countered.