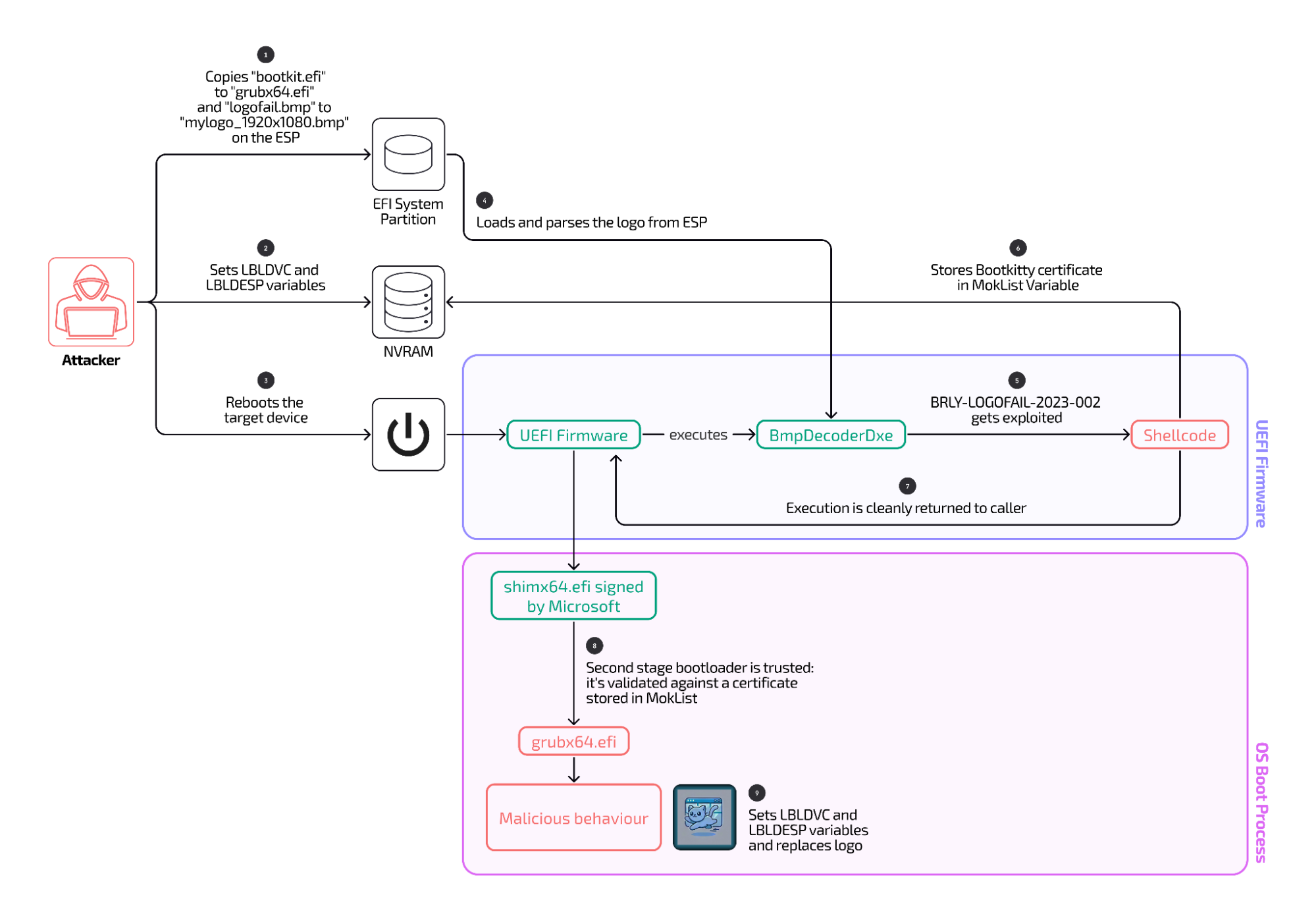
Binarly has confirmed that the recently discovered Linux UEFI bootkit, named “Bootkitty,” exploits the LogoFAIL vulnerability to target computers with compromised firmware. The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-40238 and first disclosed in November 2023, involves flaws in firmware image processing, enabling attackers to bypass security mechanisms, including Secure Boot.
ESET, the organization that initially documented the bootkit, clarified that Bootkitty was developed by students of Korea’s elite cybersecurity training program, Best of the Best (BoB). The project aimed to highlight the risks posed by UEFI vulnerabilities and encourage proactive mitigation measures. However, the developers acknowledged that certain bootkit samples were leaked prior to their scheduled conference presentation.
LogoFAIL encompasses a series of vulnerabilities in the UEFI firmware image-handling code. These flaws allow attackers to embed malicious images or logos into the EFI System Partition (ESP), thereby intercepting the boot process.
According to Binarly, the malicious file “logofail.bmp” contains shellcode embedded at the image’s end. The exploitation leverages a negative height value (0xfffffd00), which triggers an out-of-bounds write during parsing. This technique enables hackers to replace certificate lists and authorize the malicious bootloader “bootkit.efi.”
Devices unpatched against LogoFAIL remain at risk of Bootkitty exploitation. Researchers have identified Lenovo devices, particularly those utilizing Insyde firmware modules, as especially vulnerable. ESET suggests that the malware’s developers are likely testing it on their own hardware, with the possibility of expanding its compatibility to a broader range of devices in the future.
The list of affected models includes the Lenovo IdeaPad Pro 5-16IRH8, Lenovo Legion 7-16IAX7, and Lenovo Yoga 9-14IRP8. Despite over a year having passed since the disclosure of LogoFAIL, many manufacturers have yet to release necessary firmware updates.
For users of devices without available patches, the following precautions are recommended: limit physical access to devices, enable Secure Boot, secure UEFI/BIOS settings with a password, disable booting from external media, and ensure firmware updates are obtained solely from official manufacturer websites.