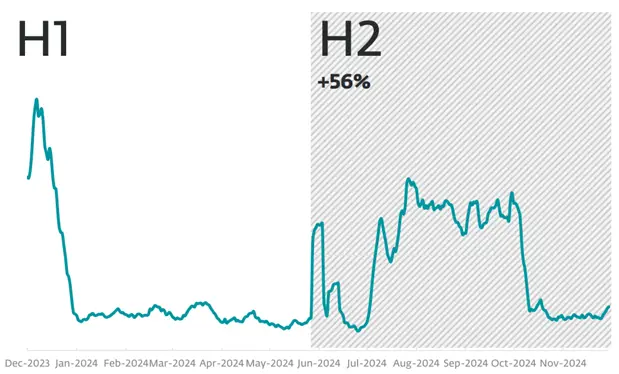
Rise in Infostealer Detections (December 2023 – November 2024, ESET Threat Report H2 2024)
In December, Bitcoin surpassed the $100,000 mark for the first time in history, surging by over 30% following the U.S. elections. The cryptocurrency’s growing popularity is likely tied to the optimism surrounding Donald Trump’s pro-digital asset rhetoric, though it has also drawn the attention of cybercriminals.
According to an ESET report, cryptocurrency thefts via malware increased by 56% in the second half of 2024. Threats were identified across all major platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Android.
Cryptocurrencies remain attractive to criminals due to their decentralization, transaction speed, and the challenges of recovering stolen funds. The FBI reports that in 2023 alone, scammers stole $5.6 billion in cryptocurrencies, with 71% of losses linked to investment fraud and 10% to phone scams.
On macOS, infections from password-stealing malware surged by 127%. Malicious software, such as AMOS and its variants, is distributed through fake Google ads, masquerading as legitimate downloads. On Windows, Lumma Stealer activity has escalated, while on Android, banking trojans now incorporate cryptocurrency theft functionalities.
A particularly concerning threat is the GoldPickaxe trojan, which targets cryptocurrency wallet users and financial service platforms in Southeast Asia. This malware can steal biometric data for creating deepfakes and bypassing authentication processes. Additionally, the Ebury botnet has been observed launching attacks on servers.
The spread of malware through phishing websites, Facebook* ad campaigns, and Telegram continues to rise. Malicious programs like Vidar and Red Line Stealer are frequently used to steal browser data and cryptocurrency wallet credentials. Cryptocurrency-related phishing sites accounted for 8% of all recorded cases.
One of the most prominent fraud schemes remains “pig butchering,” combining romance scams with investment fraud. Experts warn that overall losses from cryptocurrency scams in 2024 continue to grow.
To safeguard your assets, it is recommended to store cryptocurrency in hardware wallets, enable two-factor authentication, avoid using public Wi-Fi, keep devices updated, and verify the sources of downloaded software. Regularly monitor account activity and remain vigilant against suspicious messages and dubious offers.