Experts at Dr.Web have uncovered a new case of mass infection targeting Android-based TV set-top boxes. The malicious software, named Android.Vo1d, has affected approximately 1.3 million devices across 197 countries.
Android.Vo1d operates as a backdoor, embedding its components in the system memory of infected devices. Upon receiving commands from cybercriminals, it can covertly download and install third-party software.
In August 2024, Doctor Web was contacted by users whose Dr.Web antivirus software detected alterations in the system files of their TV set-top boxes. The issue primarily affected the following models:
- R4 (Android 7.1.2);
- TV BOX (Android 12.1);
- KJ-SMART4KVIP (Android 10.1).
In all instances, similar signs of infection were observed. The system files were either modified or supplemented with the following objects: altered files install-recovery.sh and daemonsu, as well as new files like /system/xbin/vo1d, /system/xbin/wd, /system/bin/debuggerd, and /system/bin/debuggerd_real.
The vo1d and wd files are components of the Android.Vo1d Trojan. The attackers attempted to disguise one of the components as a system program by replacing the letter “l” in the file name /system/bin/vold with the numeral “1.”
The Trojan modifies the install-recovery.sh script, which is executed during system startup, to ensure the wd component launches automatically. Additionally, the daemonsu file, responsible for providing root privileges, is altered for the same purpose. The debuggerd file, typically used for generating crash reports, is replaced with a script that initiates the wd component.
Android.Vo1d employs several methods to maintain its presence on infected devices:
- Modification of startup scripts: It alters the install-recovery.sh file, integrating its components into the system’s startup sequence.
- Exploitation of superuser privileges: It modifies the daemonsu file, associated with root permissions, to enable the malware to launch during boot.
- Replacement of system daemons: It substitutes the system’s debuggerd daemon with a malicious script to ensure its components are activated.
These techniques significantly increase the likelihood that at least one method will successfully trigger the malware during device reboot.
The primary functionality of Android.Vo1d resides in its vo1d and wd components, which work in tandem. The vo1d module initiates wd and monitors its activity, restarting the process if necessary. Both modules are capable of downloading and executing binary files, as well as installing discovered APK files.
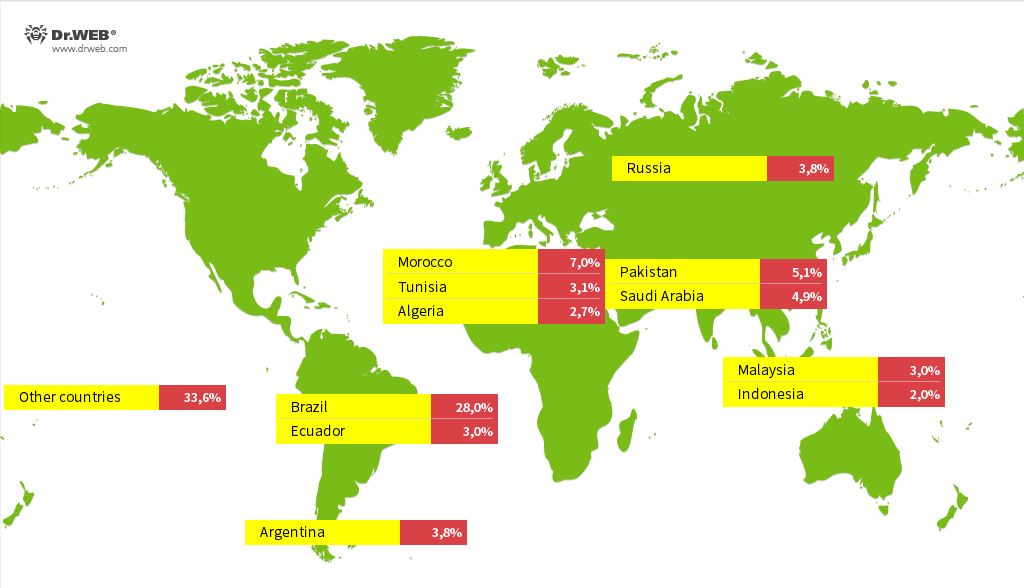
According to Doctor Web, the highest concentration of infections has been reported in Brazil, Morocco, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Argentina, Russia, Ecuador, Tunisia, Malaysia, Algeria, and Indonesia.
The source of the infection remains unknown. It is possible that intermediary malware is exploiting operating system vulnerabilities to gain root access, or that unofficial firmware versions with pre-installed privileges are being used.
One potential reason why attackers have targeted TV set-top boxes specifically is that these devices often run outdated versions of Android with unresolved vulnerabilities. Some manufacturers package older versions of the OS as newer ones to increase the appeal of their products. Users may mistakenly believe that TV set-top boxes are more secure than smartphones, and are less likely to install antivirus software on them, increasing the risk of infection when downloading third-party applications or installing unofficial firmware.