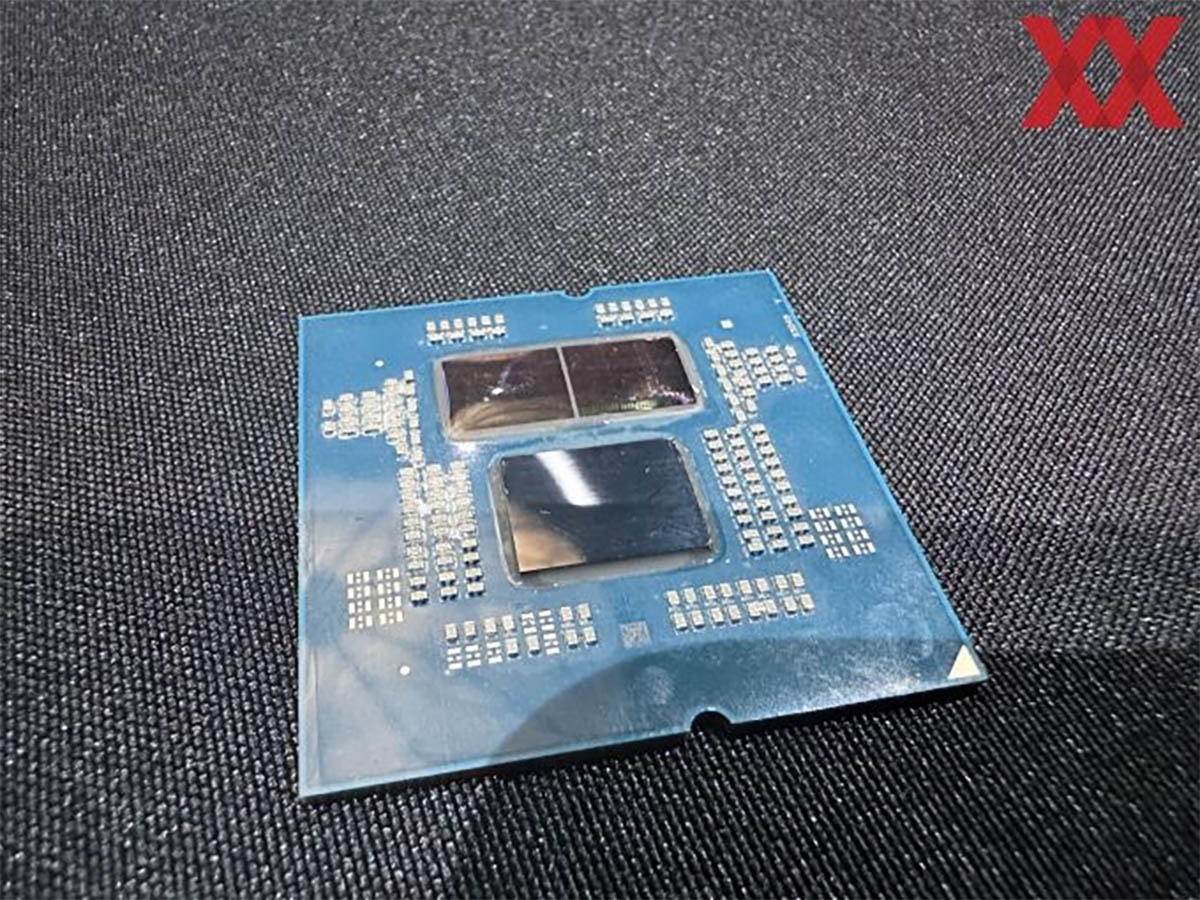

At the end of this month, AMD will unveil two new Zen 5 architecture processors: the Granite Ridge, an AM5 socket-based Ryzen 9000 desktop processor, and the Strix Point, a Ryzen AI 300 mobile processor. AMD’s presentation revealed most of the information about these two processors, two crucial details were omitted: the chip size and transistor count.
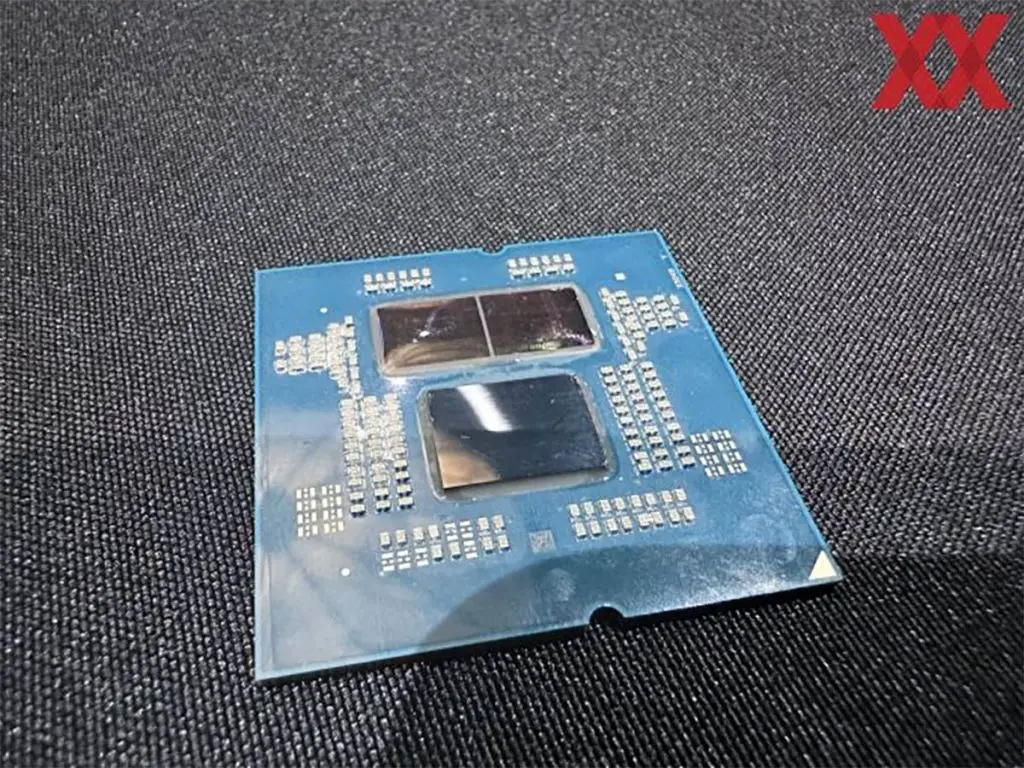

Typically, AMD discloses this data in their review guides, but HardwareLuxx.de obtained the answers during a post-presentation Q&A session. The Granite Ridge’s structure is essentially identical to its predecessor, the Ryzen 7000 Raphael, even retaining the same 6nm I/O Die with a chip area of 122 square millimeters and 3.4 billion transistors.
However, the CCD production process has been upgraded to TSMC’s 4nm (N4P) process. The Zen 5 CCD, codenamed Eldora, boasts 8.315 billion transistors and a chip area of 70.6 square millimeters. In contrast, the previous generation Zen 4 CCD Durango had 6.5 billion transistors but a slightly larger chip area of 71 square millimeters. This indicates that the Zen 5 CCD has a higher transistor count than the Zen 4 CCD, yet a smaller area, demonstrating a significant improvement in transistor density with TSMC’s N4P compared to N5, with a 26.8% increase in transistor density per unit area.
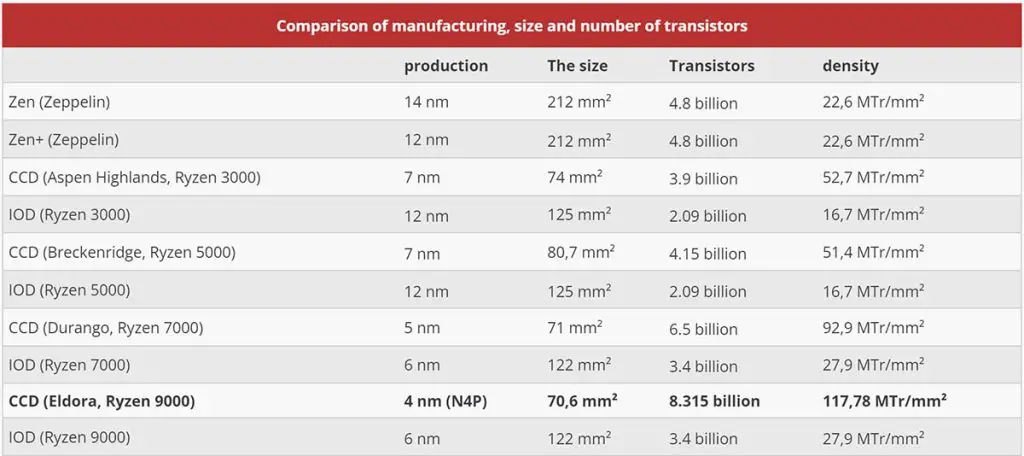
Based on these transistor counts, the dual-CCD Ryzen 9 9950X and Ryzen 9 9900X have a total transistor count of 20.03 billion, while the single-CCD Ryzen 7 9700X and Ryzen 5 9600X have 11.715 billion.
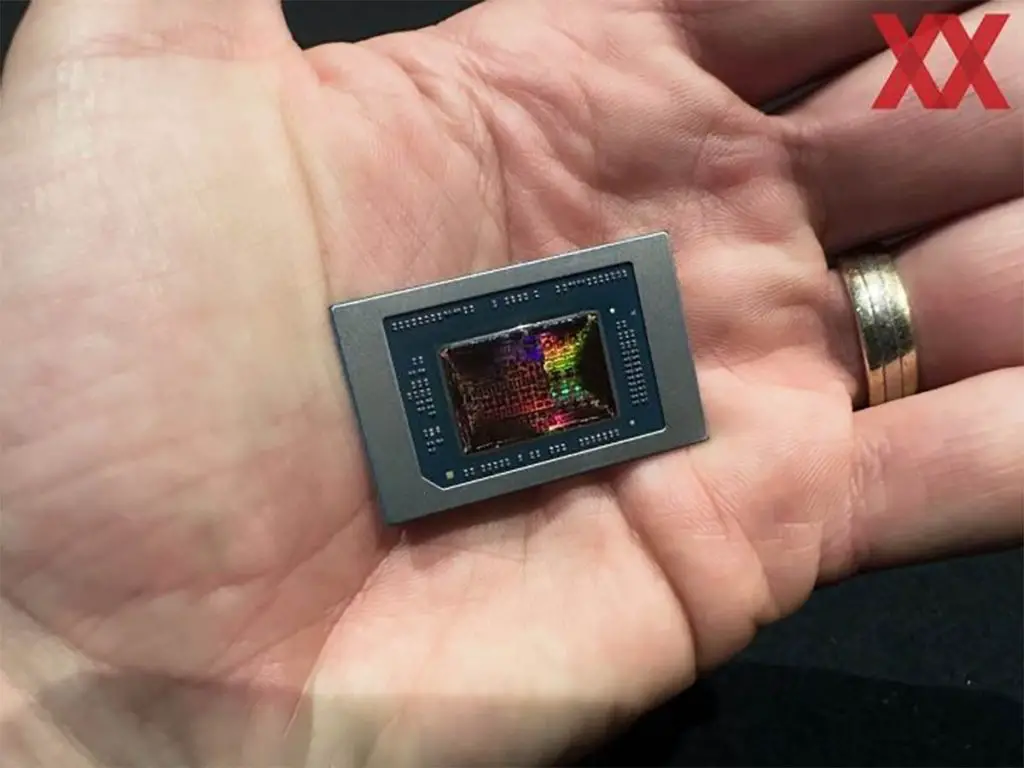

The Strix Point, a single-chip processor, also utilizes TSMC’s N4P process, representing a minor upgrade from the previous generation’s N4-based Phoenix and Hawk Point.
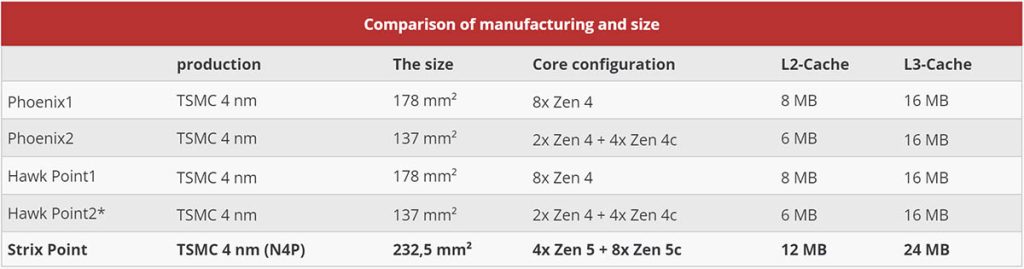
However, the Strix Point’s chip area is a substantial 232.5 square millimeters, considerably larger than the 178 square millimeters of Phoenix and Hawk Point. This is primarily due to Strix Point’s significantly higher core specifications, consisting of four Zen 5 and eight Zen 5c cores. The L3 cache capacity has also increased from 16MB to 24MB, and the GPU’s CU count has risen from 12 to 16, accompanied by a larger NPU.


