More than 12,000 GFI KerioControl firewalls remain vulnerable to the critical security flaw CVE-2024-52875, which enables remote code execution (RCE). Despite a patch being released as early as December, the issue persists, with cybercriminals actively exploiting it.
KerioControl is a comprehensive network security solution widely utilized by small and medium-sized businesses. It provides VPN services, traffic filtering, antivirus protection, bandwidth management, and monitoring. However, the ongoing exploitation of this vulnerability poses a significant threat to the security of thousands of organizations.
The security flaw was discovered in December by researcher Egidio Romano (EgiX), who demonstrated that remote code execution attacks could be launched with just a single click. The vulnerability stems from improper sanitization of user input in the dest parameter, allowing attackers to inject malicious HTTP headers and execute Reflected XSS attacks.
GFI Software issued a fix in version 9.4.5 Patch 1 on December 19, 2024, yet even three weeks later, more than 23,800 servers remained exposed. Despite repeated warnings, many companies have been slow to update, leaving thousands of KerioControl instances susceptible to attack.
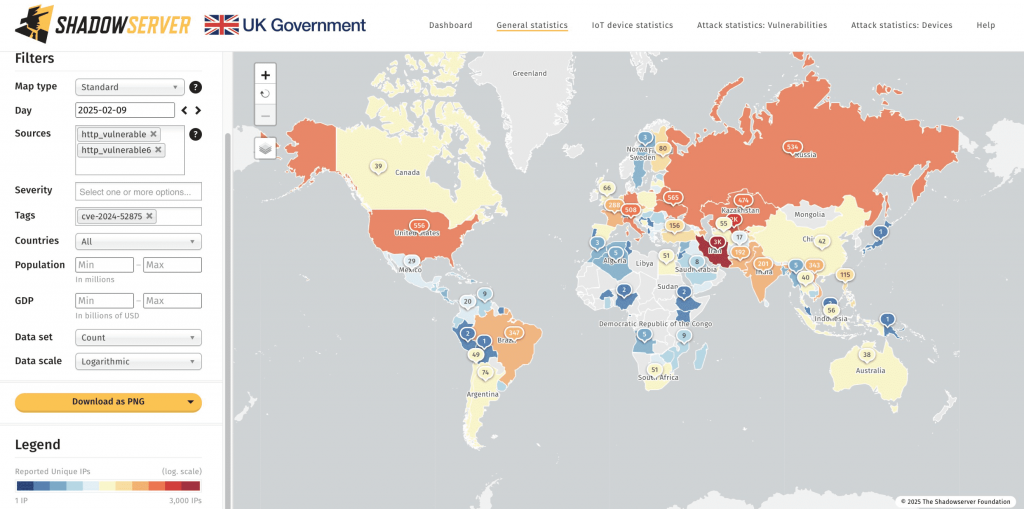
According to Greynoise, attempts to exploit the vulnerability surged in January, with hackers leveraging publicly available proof-of-concept (PoC) code to steal administrator CSRF tokens. On February 10, experts from Shadowserver reported that 12,229 compromised devices were detected in high-risk environments.
The majority of vulnerable KerioControl instances are located in Iran, the United States, Italy, Germany, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, France, Brazil, and India. Due to the low barrier to entry, attackers of varying skill levels can exploit this flaw.
Experts warn that the existence of a public exploit significantly heightens the risk for organizations relying on KerioControl. The vulnerability facilitates HTTP Response Splitting attacks, which can lead to XSS exploitation and further system compromise.
Administrators of affected servers are strongly urged to update to version 9.4.5 Patch 2, released on January 31, 2025. This update includes crucial security enhancements and additional fixes necessary to mitigate ongoing threats.


